Opioids are drugs that alter the state of mind and perception of the environment.
Sometimes opioids induce sleep, unconsciousness but does not occur even at high doses.
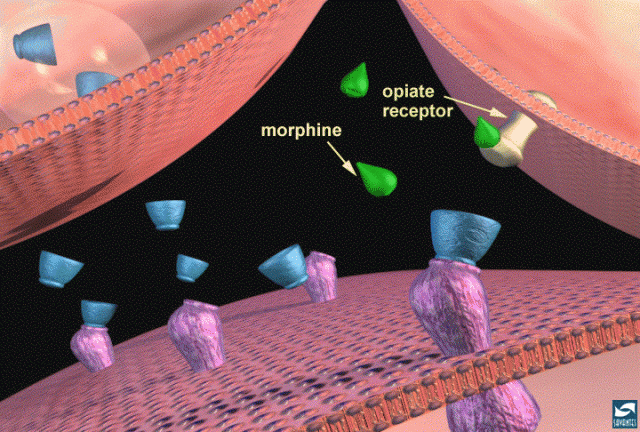
Opiates have diverse chemical structure, but rather produce similar effects, due to the fact that they bind to specific “opioid” receptors.
The main effects of opiates are:
- Analgesic activity, a strong reduction in pain of any origin.
- Euphoric activity, the ability to cause a particular mental state of well-being and complacency.
- Suppressing the cough and respiratory centers of the brain.
- Activation of the parasympathetic system, constriction of the pupils.
- Increased bowel tone, constipation, spasms of smooth muscles.
- With prolonged use of opiate activity decreases (tolerance).
- Unpleasant effects of the sudden cancellation of the drug (abstinence or breaking).
- Opioids cause psychological and physical dependence (addiction).
According to the chemical nature, the nature and mechanisms of modern analgesics pharmacological activity is divided into two main groups:
- Opioids – morphine alkaloids similar to it (opiates) and synthetic compounds having morphine-like properties.
- Non-opioids – synthetic derivatives of salicylic acid, pyrazolone, aniline, and others.
Opioids are considered the most dangerous of all types of drugs.