What is Chickenpox?
 Chickenpox is an infectious disease that can cause mild fevers and a rash of itchy inflamed blisters. It is caused by the herpes zoster virus that is mostly prevalent in children, who afterwards become immune to a further outbreak. Chickenpox is very common in children. Most people think that Chickenpox is a mild disease; however it is recommended that one should still get vaccinated to avoid further complications. This vaccine is very safe and helps to prevent one from getting the disease.
Chickenpox is an infectious disease that can cause mild fevers and a rash of itchy inflamed blisters. It is caused by the herpes zoster virus that is mostly prevalent in children, who afterwards become immune to a further outbreak. Chickenpox is very common in children. Most people think that Chickenpox is a mild disease; however it is recommended that one should still get vaccinated to avoid further complications. This vaccine is very safe and helps to prevent one from getting the disease.
Symptoms of Chickenpox:
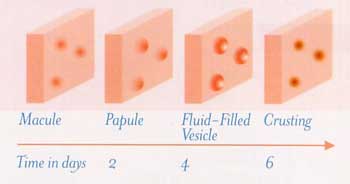
- The most common recognized chickenpox symptom is a spotty, blistering red rash that may cover the whole body.
- A low-grade fever;
- Some discomfort, illness or lack of wellbeing;
- Ulcers may form in certain areas of your body, including the mouth
Chickenpox spots
The spots will typically appear in groups and tend to be:
- Behind the ears;
- On the face;
- Over the scalp;
- On the chest and stomach;
- On both of the arms and legs;
Causes of Chickenpox
- Chickenpox is spread by airborne droplets from the upper respiratory tract (when the infected person coughs or sneezes) or by touching the matter from blisters on the skin and after that coming into contact with a healthy individual.
- It often takes 14 days for all the symptoms of chickenpox to show after you have come into contact with the virus.
Treatment for Chickenpox
- There is no cure for Chickenpox; it usually clears up by itself, without any treatment.
- Painkillers; If your child is in great pain or has a high temperature, you may give them a mild painkiller;
- Keep hydrated; It is important for those with chickenpox to drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
- Chickenpox can be very itchy – One way of stopping scratching is to keep fingernails as clean and short as possible as there are numerous germs located under the nails.
- Wear cool clothing – If you have a fever, or if your skin is sore, dress appropriately so that they do not get too hot or too cold. Use clothes that are loose fitting and comfortable as this will not make your body itch.
- Ensure you have plenty bed rest.
- Take lukewarm baths to relax yourself, soothe your skin and to help prevent blisters from burning.
The possible complications of chickenpox include
- Bacterial infections of the skin, soft tissues, bones, joints or bloodstream;
- Pneumonia;
- Inflammation of the brain;
- Toxic shock syndrome;
- Chickenpox can leave pockmarks and dark scars on the skin;
- Cellulitis is a type of bacterial infection of the skin;
- Bleeding disorders are rare, but can be fatal;
- Death, but this is very rare;
Who is at risk?
Those at high risk of complications from Chickenpox include:
- Newborns and infants whose mothers have never had chickenpox or the vaccine;
- Adults;
- Pregnant mothers who haven’t had chickenpox;
- People who have a weakened immune system;
- People who are taking steroid medications for another condition such as children with asthma;
- People who take drugs that suppress their immune systems.
