CHAPTER 2 ACCOMPLISHMENTS OF THE AIDS RESPONSE
| Reports - HIV/AIDS in China Report 2007 |
Drug Abuse
CHAPTER 2 ACCOMPLISHMENTS OF THE AIDS RESPONSE
The 2004 Joint Assessment (JAR) and the 2005 Update on the AIDS Epidemic and response in China highlighted a number of challenges hindering effective AIDS prevention, treatment and care in China. These included the need for strong leadership and political commitment from all levels of government, legislative reform, information exchange and utilization, improved in surveillance systems, improved advocacy and education interventions, strengthened monitoring and evaluation and increased financial support. The years 2006 and 2007 have seen obvious progress on responding to these challenges, which are highlighted in this report.
2.1 Government Commitment and Leadership Building
The 2004 JAR identified uneven implementation of the AIDS response across ministries and provinces. Cross-sector cooperation was only superficial, while a number provinces and sectors did not have strategic plans in place, provincial plans were at different stages of development and mechanisms to monitor and evaluate performance were weak.
In the past two years, the Chinese Government gave high priority to expanding the response at all levels to AIDS prevention, treatment and care, and ensuring more effective implementation of the programme.
2.1.1 The legal and policy framework has been strengthened
The Regulation on AIDS Prevention and Treatment (Decree No. 457) was issued by the State Council in early 2006. The Regulation was the first legal framework developed in China for a specific disease or epidemic. This provides a legal framework for AIDS initiatives, emphasising the accountability of governments and Ministries at different levels. They also set out the rights and responsibilities of people living with HIV, ensure the funding of AIDS measures and provide the legal foundations for AIDS policy formulation and its effective implementation.
China has actively followed 'Three Ones' principle—One national plan; One coordinating mechanism; and One monitoring and evaluation (M&E) system. The State Council AIDS Working Committee has established 'one national coordinating mechanism'. China's Action Plan for Reducing and Preventing the Spread of HIV/AIDS (2006-2010), issued by the State Council Office in March 2006, provides one national planning framework, while the release of China's AIDS Monitoring & Evaluation Protocol in June 2007 provided the third pillar.
Research into the prevention and control of AIDS and other focal infectious disease is one of 16 priority tasks in 'China's Development Programme of mid- and long-term Science and Technology Development (2006 -2020)'.
The Ministry of Civil Affairs, the Ministry of Justice, the Ministry of Railways, the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection & Quarantine, General Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, All China Trade Union, the Red Cross Society of China and other sectors have developed action or strategic plans to respond to AIDS.
Yunnan, Zhejiang, Shandong and some other provinces formulated their local AIDS prevention regulations or measures, while each province developed their own 5-year action or implementation plans for 2006-2010.
2.1.2 National leadership is setting the example
The Chinese Government leaders demonstrated their commitment to AIDS prevention and set examples through personal actions with people affected by the disease. On 1 December 2006 Premier Wen Jiabao and Vice-Premier Wu Yi invited 17 children orphaned by AIDS and living with HIV, together with doctors and teachers from Henan, Yunnan and other provinces as guests of Zhong Nan Hai and to attend the 'Our Care-Attention to Children Orphaned by AIDS-Evening Gala Concert'. Premier Wen Jiabao took the lead in donating to children orphaned by AIDS.
2.1.3 Increased financial commitment
In recent years the Central Government financial input to AIDS prevention and care has been significantly increased. Central government resources devoted to AIDS was RMB 854 million in 2006, which increased to 944 million in 2007. In accordance with the incomplete data from local AIDS Working Committee Office, local financial commitments showed a corresponding increase.
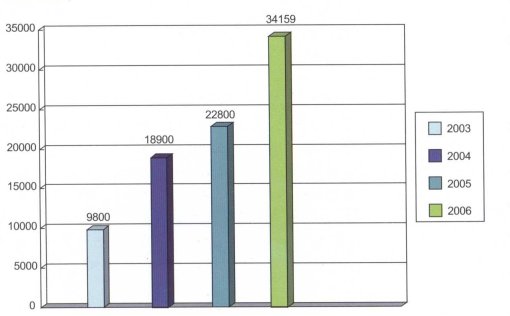
Figure 2.1 AIDS budget contributions by provincial governments 2003-2006 (10,0(J0 Yuan, incomplete data)
2.1.4 Strengthening awareness of leadership
The State Council AIDS Working Committee Office (SCAWCO) organised workshops on the Regulations and the Five-Year Action Plan to brief leaders on their implications for implementation and learning requirements. SCAWCO conducted a series of training activities on HIV policy. The initial presentation was made at the Central Party School in June 2006, and was extended nationally through the Schools' long distance education network broadcast. In this way, 100,000 political and government leaders were reached in local Party Schools.
The HIV Policy Advocacy Group then travelled to 16 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) where presentations were made, while at the same time some provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities), including Zhejiang, Shanxi, Hubei, Sichuan, Guizhou and Xinjiang, organised local HIV policy promotion teams to conduct publicity activities at local levels.
The Central Department of Publicity and other agencies held two workshops for publicity department personnel nation wide, including 19 major national media outlets. In follow up through the Central Party School, over ten local Party Schools integrated HIV policy and knowledge into their curricula for leaders at various levels. The National Administration College of the Ministry of Education, party schools of the Ministry of Communications and of the State Administration of Industry & Commerce also integrated HIV policy and knowledge into their training curricula.
2.1.5 Cross-sector cooperation has been strengthened
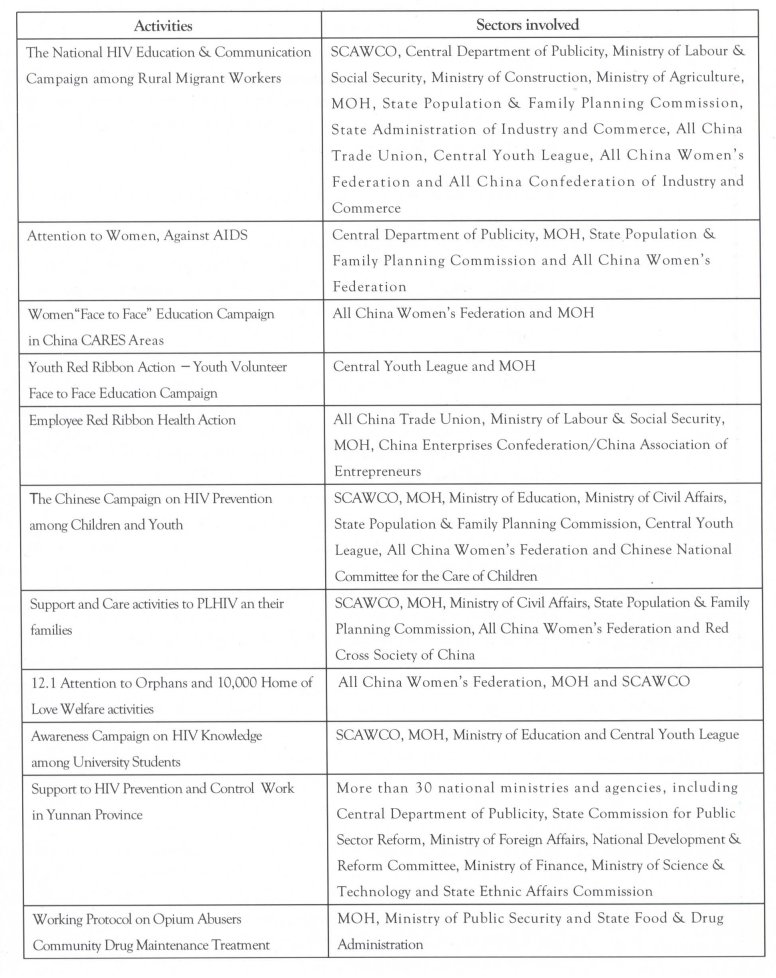
During the past two years, there has been significant advancement in the coordination and cooperation across sectors. Various large-scale initiatives were jointly conducted, which are summarized in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1: Summary of Key Cross-sector Initiatives
2.2 All Society Involvement
The 2004 JAR noted that was limited involvement of community-based organizations and they were weak in terms of capacity in implementation and management of projects, particularly at the local level.
More and more mass organizations, civil society organizations and enterprises and business are actively involved in the national response to AIDS over the past two years. Their range of involvement has become broader in its scope anc depth and they have become an important player and indispensable force in the national response to the epidemic.
2.2.1 Government advocacy and support for civil society involvement
The Regulation on AIDS Prevention and Treatment decrees that national government encourage and support organizations, including Trade Unions, Youth Leagues, Women's Federations and Red Cross Societies, to take cooperative activities on AIDS prevention and treatment with various levels o people's government. It encourages and supports relevant organizations anc individuals to participate in AIDS prevention and treatment in accordance with the Regulation and the national programme and action plan on AIU prevention and control.
The Central Government has established special funds for social mobilizatioi for AIDS, while utilizing international cooperation funds, especially the Globa Fund, to support the involvement of mass organizations and civil society groups In the four years 2002 to 2006, some 287 social mobilisation projects fron across China were approved, with funding amounting to 26.9 million Yuan.
The Global Fund Rounds 3, 4 and 5 provided total support to civil societ organizations of 43 million RMB. The newly approved Round 6 has earmarked US$10.08 million for civil society activities, some 70 per cent of the total budge for this round.
2.2.2 Mass organisations and civil society participation
Many national level mass organizations and civil society groups are activel involved in HIV work and are providing support for the development and capacity building of community-based groups. Provincial STD/AIDS associations have also been strengthened. By the end of October 2007, STD, AIDS associations had been established and further developed in 18 provinces, while many districts and cities had also been motivated to establish STD/AIDS associations.
Civil society organizations and community-based groups are implementing an increasing number of AIDS interventions at various levels. The number of community-based groups, including PLHIV support groups, women's groups and most-at-risk intervention groups increased from around 100 to over 400 by 2007. More than 6,000 volunteers are working within MSM community groups nationwide at the present time.
By participating in project design, implementation and monitoring, the initiatives and commitment of community-based and PLHIV groups continues to be strengthened, which reflects the GIPA principle. Some civil society organizations played an active role in the Global Fund Country Coordinating Mechanism (CCM) reforms.
The faith-based organizations, such as Buddhist, Islamic and Christian groups, also participated in the HIV awareness campaigns and support activities in Xinjiang, Yunnan, Ningxia, Shaanxi, Hunan, Liaoning and other areas.
ART Compliance Education by Farmer's Health Group
In Xincai County, Henan Province, 25 PLHIV volunteered to form a Farmer's Health Group and carried out various support activities, including AIDS awareness, 01 treatment and ART compliance education, promotion of family-based nutrition, care and psychosocial support. Over the past two years, their face to face communication sessions reached over 1,200 contacts. They used their personal experiences to demonstrate the change before and after ART and convinced other PLHIV and their family members of the importance of standardized drug-taking and improved their compliance to the ART.
2.2.3 Enterprise and business involvement
In June 2007 SCAWCO issued a Notification on mobilizing business commitment to and participation in HIV prevention. The Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Taxation issued a taxpayer deduction policy for donation to HIV prevention and AIDS care activities.
The All China Confederation of Industry & Commerce, the China Enterprises Confederation (CEC), the China Private Business Association and the Global Business Coalition (GBC) on AIDS all played an active role in coordinating the involvement of enterprises in the AIDS response.
After the Summit of Global Business against AIDS in Beijing in 2005 - co-organised by the Chinese Government and GBC - many enterprises increased their efforts in workplace AIDS education programmes to promote knowledge and awareness, and developed workplace AIDS policies to reduce stigma and discrimination.
Businesses also provided financial and in-kind donations of 28 million RMB through various channels. Pharmaceutical enterprises were actively involved in the development and production of ARV drugs, giving strong support to the ongoing development of ART Some enterprises cooperated with the government to undertake comprehensive campaign on HIV prevention and control.
2.2.4 Role of celebrities
In 2006 SCAWCO held a seminar titled 'United Celebrities, Media and Businesses against AIDS'. In follow up with the Goodwill Ambassadors for AIDS - Pu Cunxin, Xu Fan, Zhou Tao, Zhang Chaoyang and Cai Guoqing, celebrities in arts and sports, such as Peng Liyuan, Li Danyang, Jiang Wenli, Yao Ming and Hou Yaowen also joined the HIV awareness campaigns. The Goodwill Ambassadors were actively involved in policy lectures, education activities and charity performances for migrant workers, children, youth and university students. They also posed for posters, public service announcements and charity songs. Ambassadors travelled to grass-roots locations to visit PLHIV and children orphaned by AIDS, visited detoxification and re-education centres through labour, and entertainment venues to promote HIV knowledge. The celebrity status of the ambassadors drew widespread interest and expanded the coverage of these events.
2.3 Comprehensive HIV Prevention Responses
The 2004 JAR noted that overall awareness of HIV remained low and that stigma and discrimination was a constraint. It found that IEC intervention needed to be improved in terms of its depth, breadth and innovation. The coverage of targeted interventions was limited, with few effective models or 'best practices' for reaching specific high risk behaviour groups and to improve the quality of existing interventions, such as 100 per cent condom use promotion, MMT and needle exchange. Further efforts were required to guarantee blood safety and reduce iatrogenic infection.
2.3.1 HIV awareness initiatives
2.3.1.1 General population HIV awareness campaigns
For the 2006 World AIDS Day, SCAWCO, the Central Department of Publicity, the State Administration of Radio, Film and Television and other ministries jointly organised the 'Our Care Evening Gala Concert', which were broadcast by CCTV channels. The programs 'Road to Health: Three Supports into Countryside-A Special Program on AIDS', a 100-part TV program 'Red Ribbon' and a World AIDS Day special program, 'Red Ribbon-Our Commitment' and Symphony-'Floating Red Ribbon' were broadcast by CCTV. The Qu Opera-'Floating Red Ribbon', presented by Henan Qu Opera Troupe, toured 14 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) over a six-month period and reached a total audience of 300,000. In addition, Ping Opera-'Red Ribbon Flying', presented by the Hebei Dachang Ping Opera Troupe, travelled to 20 provinces and performed at over 70 sites.
The Central Department of Publicity launched large-scale 'Red Ribbon' campaigns in Yunnan, Xinjiang, Shaanxi, Guizhou, Gansu and Sichuan. On-line discussions were also conducted on major websites, including Xinhua, on issues of children orphaned by AIDS, HIV prevention among university students and migrant workers.
The State Administration of Radio, Film and TV, the State Council Information Office and others actively organised and coordinated the media to report on AIDS related issues, with extensive coverage achieved by radio, television, films, newspapers, journals and websites to promote HIV knowledge.
Various sectors, including railways, communications, civil aviation and border control and quarantine regularly developed and published public billboards and exhibits panels on HIV knowledge at bus stations, shipping ports and airports; and also initiated education activities to their passengers. All public places in China CARES areas have large billboards and every village has publicity slogans on the walls.
2.3.1.2 Focal populations
SCAWCO and related ministries conducted a number of advocacy campaigns targeted to migrants, youth, women and minority populations. A wide range of IEC materials, such as prints, visual products and substantial materials, were designed and produced. Some IEC materials were translated, produced and disseminated in nine minority languages, including Uygur, Ha, Mongolian, Zang (Tibetan) and Korean. The State Ethnic Affairs Commission conducted a situation analysis and response research on HIV prevention and control in minority areas. The Commission produced video programs on HIV awareness in minority languages.
(a) Children and youth
The 'Chinese Campaign on HIV Prevention among Children and Youth', was launched in September 2006. The Ministry of Education and the MOH developed, printed and disseminated key messages and material on HIV for children and youth.
A HIV awareness campaign for university students themed 'Against AIDS for a Wonderful Campus' was jointly launched by SCAWCO, the Ministry of Education, MOH and the Central Youth League in June 2007. A Students Reading Booklet on HIV Awareness was compiled and printed; a national university students' lecture competition on HIV knowledge was held and university students were recruited for voluntary participation in the face to face education campaign.
The Ministry of Education equipped over 4,000 schools with AIDS education materials. Specific trainings on HIV knowledge was presented to more than 10,000 teachers and was also integrated into pre-employment trainings for the graduates of teacher's colleges. National field visits and seminars were organized and online quiz on HIV awareness of young people was conducted, with more than 18 million visits.
The Central Youth League launched an awareness campaign entitled Youth Red Ribbon. It is estimated that over 14,000 youth joined the in-school peer education network in 2006. More than 200,000 youth joined the face to face communication and 3.2 million youth were covered through the internet.
(b) Migrant workers
Following the launch of the National HIV Education & Communication campaign among rural migrant workers in 2006, relevant ministries developed their annual work-plans and established 6,071 leading groups on HIV communication initiatives for migrant workers within their field of work. SCAWCO, the Central Department of Publicity, Ministry of Construction, MOH and the Beijing AIDS Working Committee jointly organized performances-'Hand-in-Hand against AIDS'-for Migrant Workers at construction sites in Beijing.
The Ministry of Labour & Social Security (MOLSS) distributed IEC materials, such as pamphlets and posters at training centres or vocational referrals with concentrated migrant workers. The Ministry of Construction initiated HIV knowledge training and education for some 1,000 management personnel, conducted training for 30,000 migrant workers by using part-time schools in six provinces and five cities, including Hunan and Jiangxi, and trained 1,500 peer educators. A reading booklet-'Common Knowledge for Migrant Workers at Construction Sites'-incorporating HIV knowledge was compiled and 100,000 copies was distributed.
The Ministry of Agriculture conducted an awareness campaign-'Red Ribbon into Village and Household'. In 2006, the 'Sunlight Campaign' directly trained 3.5 million rural people and over 5 million people received indirect training on HIV awareness. The Ministry had more than 30 articles on HIV prevention published in the Farmers' Daily newspaper.
The State Population & Family Planning Commission integrated HIV knowledge into the family planning IEC materials for migrant populations, compiled and distributed 100,000 copies, with focus on the six provinces with large numbers of migrant populations, such as Henan.
All China Trade Union initiated campaigns on HIV knowledge into thousands of workplaces, covering over 10,000 evening schools and reached 3 million migrant workers. Its Art Troupe travelled to Hebei, Guangdong, Henan and other provinces and presented over 20 performances with 80,000 viewers. The Youth League conducted Youth Red Ribbon campaign on promoting HIV awareness while film showing at the workplaces, covering nearly 400,000 migrant workers, and more than 300,000 copies IEC materials was distributed.
The Ministry of Railways set up billboards at 270 railway stations and initiated station-based education activities. They also conducted on-train HIV education on special trains for migrant cotton pickers. The General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection & Quarantine initiated AIDS education and behaviour intervention at 420 frontier ports, reaching 1 million contract workers sent abroad.
(c) Women
The All China Women's Federation (ACWF) launched a national programme on 'HIV Prevention for a Healthy Family', which targeted housewives to empower their families for HIV prevention and care.
The ACWF expanded the face-to-face education activities into 127 China CARES areas, over 120,000 volunteers were organized, 9,710,000 participants were trained, and 27.25 million women were exposed to various HIV information and education activities, accounting for 67 per cent of the total female population in the China CARES areas. Of those reached women, 16.52 million were aged 15-49, 83 per cent of the cohort. The HIV awareness rate reached 81 per cent among the target women, and 92 per cent among those between 15 and 49 years old. In 2007, the HIV face to face education approach was extended to an additional 148 counties covered by the Global Fund projects.
(d) In the work place
The Ministry of Public Security conducted trainings on HIV policy and knowledge through long-distance education network, reaching more than 100,000 policeman nation-wide. The Ministry of Public Security and the Ministry of Justice conducted training for officials working in closed settings.
The MOLSS integrated HIV knowledge into their training curriculum of vocational schools and provide free training materials to 11 provinces. MOLSS and CEC launched the HIV Workplace Education Programme in three pilot provinces to reduce workplace stigma and discrimination and increase coverage of workplace intervention.
The Ministry of Railways provided HIV training to 5,700 leaders, 3,400 health care professionals and 160,000 of its staff across China. Similarly, the Ministry of Communications and the ACWF jointly promoted HIV awareness activities for their staff and family members.
The Ministry of Commerce integrated HIV knowledge into their regular training courses for personnel assigned to working abroad. They also conducted HIV awareness campaigns through exhibits, picture journals and newsletters.
The State Population & Family Planning Commission conducted training on HIV knowledge, policies and their responsibilities in the AIDS response and the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection & Quarantine conducted trainings on HIV knowledge and policies to its 36,000 staff. The General Administration of Civil Aviation held three training courses on HIV knowledge to their doctors.
The State Administration of Industry & Commerce set up a task force on HIV Prevention with over 30,000 focal points and conducted training to focal points at provincial level. They also explored education models which work for private sectors with concentrated migrant workers. All China Trade Union held training coursed for over 200 chairs of trade unions at middle sized enterprises and above across prefecture level in 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities).
The armed forces followed a central plan to educate their mass employment base in AIDS related issues.
2.3.2 Behaviour change interventions among most-at-risk populations (MARPs)
2.3.2.1 Sex workers (SWs) and their clients
In 2006, four provinces—Hubei, Hunan, Yunnan and Hainan—conducted condom use promotion campaigns at entertainment places across the whole province. Other provinces (autonomous regions), such as Xinjiang, Guizhou, Shanxi, Sichuan, Guangxi, Jiangsu, Fujian, Zhejiang and Shandong, also conducted similar campaigns across relatively large areas. All 127 China CARES areas launched comprehensive interventions, mainly focused on condom promotion. The coverage of intervention programmes for SWs and their clients had been expanded to all counties by 2007. Interventions reached 462,357 SWs by the third quarter of 2007. Thus, intervention coverage for SWs increased to 38 per cent from only 26 per cent in 2005.
The national behaviour surveillance survey data showed that the rate of female SWs using condoms every time in commercial sex during the last month had increased from 14.7 per cent in 2001 to 41.4 per cent in 2006. The rate for SWs never using condoms decreased from 37.4 per cent in 2001 to 7.5 per cent in 2006. The change since 1995 is illustrated in Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2 Condom use among sex workers, 1995-2006 (National Behaviour Surveillance Survey Data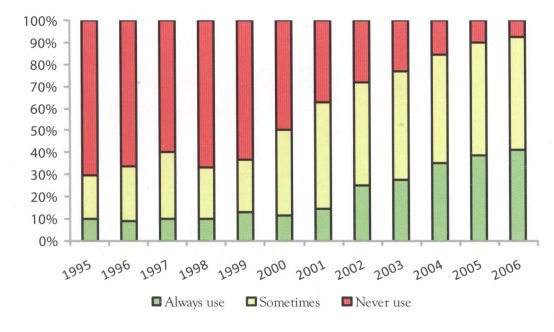
2.3.2.2 Injecting drug users (IDUs)
In July 2006 the MOH, Ministry of Public Security and the State Food & Drug Administration revised and issued the Opium Abusers Community-Based Drug Maintenance Treatment Protocol, which highlighted the expansion of the MMT programme from the pilot phase to general application. By the end of October 2007, 397 MMT clinics were open in 22 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). By now, 88,313 drug users had joined the MMT treatment program. Among 51,758 participants who are now on treatment, the annual retention rate is 64.5 per cent. The clinics also provide free HIV testing and counselling service on a regular basis to all individuals who joined the MMT program.
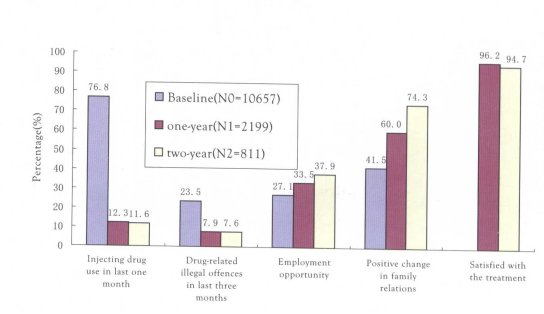
The evaluation survey to some of the MMT clinics conducted in 2007 found positive change in the rate of injecting drug use, drug-related illegal offences, employment opportunities and family relations as shown in the Figure 2.3.
Figure 2.3 Participant response to MMT
In 2006, a total of 729 needle exchange stations have been established in 204 counties or districts in 17 provinces. By third quarter of 2007, about 49,108 IDUs had joined clean needle exchange programmes.
2.3.2.3 Men who have sex with men (MSM)
Since 2005, the Chinese Government has strengthened its intervention efforts to MSM, developed national working protocols and guidelines on HIV prevention and control among MSM, and convened national technical workshops on comprehensive HIV prevention interventions among MSM. Various programmes were conducted on condom promotion, counselling and testing, peer education, STI services and follow-up outreach and care services for PLHIV. The third quarter 2007 statistics showed that 88,082 MSM were reached by comprehensive HIV prevention interventions, a coverage of around 8.2 per cent of the MSM population.
MSM interventions by CDC and community-based organisations
Chengdu CDC in Sichuan Province has worked with Chengdu Tongle Health Counselling Service Centre to conduct interventions among MSM, such as setting up volunteer groups among university students, middle-aged or elders and internet-connecters, conducting capacity building and some small-scaled activities, by taking advantage of the frequent daily communication between MSM sub-groups. Based on different group's respective interests and behaviour, appropriate peer education models were explored. CDC provided technical support and monitoring and evaluation support to the interventions, and intensified VCT services to the MSM population by expanding sentinel sites and VCT sites on the platform provided by Tongle.
2.3.3 Strengthened blood safety management
Nationwide advocacy of voluntary donations was maintained. The clinical use of non-paid donated blood has increased from 22 per cent nationwide in 1998 to around 98 per cent in mid-2007, of which voluntary blood donations were 5.5 per cent in 1998 and reached 95 per cent in mid-2007. By then, 100 cities had achieved 100 per cent clinical blood use from voluntary donation.
Implementation of the 2007 Working Protocol on National Enforcement against Illegal Blood and Plasma Collection enhanced supervision of plasma donation stations, ensured the well-being of plasma donors and quality control of the blood and plasma collected. The blood quality supervision and control systems at blood stations, plasma collecting stations and blood product manufacturing units were further strengthened.
2.3.4 Prevention of mother-to-child transmission (PMTCT)
Guidelines for strengthening PMTCT were developed and released in 2006. PMTCT activities have been expanded to 271 counties in 110 prefectures in all provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). PMTCT was integrated into women's and infants' health care at provincial level on the basis of the three-level health network for women and infants. In addition, PMTCT services were provided concurrently with pre-natal services.
By the end of December 2006, surveys of PMTCT programmes had covered more than 2.65 million pregnant women, 77.7 per cent of whom received AIDS counselling, while the testing rate was 74 per cent. The cumulative number of HIV positive pregnant women was 2,706. Among women with HIV who delivered, 72.4 per cent received ARV drugs and the rate of ARV treatment for their babies was 80.4 per cent. The non-breast feeding rate is 84.6 per cent. The AIDS transmission rate from mother-tochild decreased nearly 60 per cent through the prevention measures.
2.3.5 Voluntary counselling and testing (VCT)
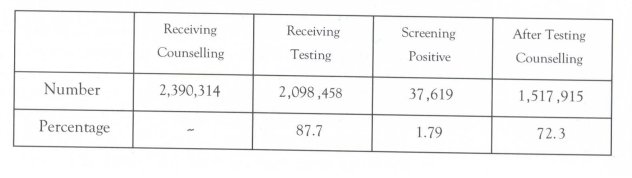
4,293 VCT stations had been established nationwide. Of these, 803 are VCT clinics in hospitals, accounting for 19.1 per cent. The service coverage of the clinics is presented in Table 2.2.
Table 2.2 VCT coverage, January 2006 to September 2007
2.3.6 STI prevention and treatment
MOH issued notification on further strengthening STI surveillance in 2007 and revised the national STI Monitoring Protocols and Guidelines. STI monitoring sites have been increased from 26 to the current 105. Various locations strengthened STI surveillance, incidence rate and epidemiological surveys and quality control of the STI testing laboratory was further improved. MOH also developed drug-resistance monitoring and provided guidelines on STI clinic medicine.
Management of STI clinics was strengthened and STI clinic treatment and counselling services were standardized. Syphilis screening and control was strengthened in health facilities providing STI clinical services, while awareness and education programmes on STI and HIV prevention were expanded. Integration of condom promotion with standardized STI clinic services was expanded to facilitate targeting interventions to most-at-risk populations.
2.4 Treatment, Care and Support
The 2004 JAR reported that the provision of affordable and accessible ARV therapy that patients can tolerate and doctors can readily supervise was a key challenge.
2.4.1 Antiretroviral treatment (ART)
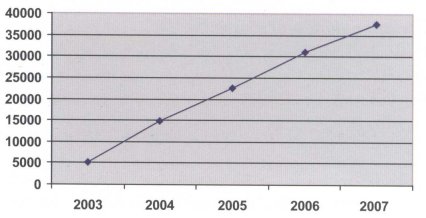
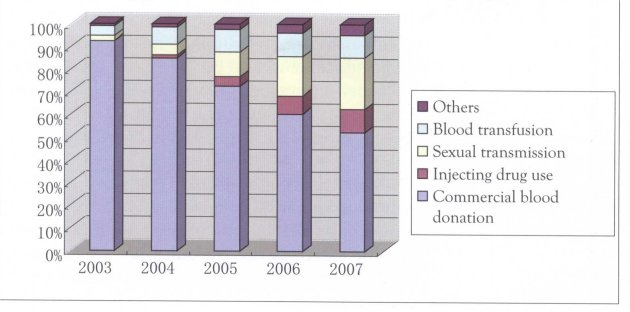
By the end of October 2007, the provision of ART was expanded to 1,190 counties in 31 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). The cumulative number of people aged 15 and above who commenced treatment was 39,298 with 31,849 currently receiving ART. The proportion of ART patients who was infected via sex transmission has increased from 4.9 per cent in 2004 to 22.7 per cent in 2007, while via injecting drug use increased from 1.0 per cent in 2004 to 10.7 per cent in 2007, as illustrated in Figures 2.4 and 2.5. The pilot project of second line drugs treatment was launched.
Figure 2.4 Cumulative number of AIDS patients receiving ART
In 2005, MOH launched a pilot project to provide ART to children below 15 years. By the end of October 2007, a total of 805 children from 141 counties and districts of 22 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) had received ART, with 761 remaining on ART.
By now, 13 clinical training centres and one clinical laboratory training centre have been established with some 1,500 technical staff trained from 447 counties or districts in 28 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities). A national AIDS patient management database was established, which provides complete linkage between the treatment database and the epidemic database.
Surveys of former blood and plasma donors in the six provinces of Central China showed the mortality rate of PLHIV decreased from 28.8 per hundred person-year before the launch of ART, to 6.8 per hundred person-year following treatment. In the survey areas the death rate of PLHIV was 3.4 per 100 person-year in 2006.
Figure 2.5 Transmission mode distributions among cumulative AIDS cases receiving ART (2003 - 2007)
2.4.2 Opportunistic infection (0I) treatment and traditional Chinese medicine
Free CH treatment is provided in some provinces. By June 2007, over 36,000 PLHIV had received OI prevention and treatment services in areas covered by the Global Fund projects.
Pilot projects on case finding and treatment for HIV/TB co-infection patients have also been developed. They provide early diagnosis of active TB among PLHIV, while conducting HIV testing among TB patients, together with co-infection treatment and management.
An advisory committee and an expert group on Chinese traditional medicine and HIV were established to amend the evaluation protocol for clinical use of traditional Chinese 'medicine (TCM) for AIDS patients. The project has been extended to 15 provinces, where over 6,000 patients are receiving this treatment. Under the treatment, most patients' status has improved and some of them can return to work.
2.4.3 ARV drug supply and resistance monitoring
With the coordination and joint efforts by SCAWCO, the Ministry of Finance, the State Administration of Taxation, the National Development & Reform Commission and the General Administration of Customs, the State Council maintaining customs exemption for the import of ARV drugs and approving tax exemptions for the local production of ARV drugs in 2007. The exemption helped stabilize the price of ARV drugs and the price of some drugs decreased. As the number of paediatric cases increased, some paediatric drugs have been included in the plan for domestic production.
A national network to monitor drug resistance was set up. Three nationwide surveys on drug resistant HIV strains have been completed. At the same time, pilot sentinel surveillance of drug resistant was initiated to detect early warning of drug resistance. The monitoring results suggested that approximately 17 per cent PLHIV on ART develop drug resistance.
2.4.4 Care and support
In order to strengthen support to PLHIV and their families, SCAWCO, MOH, Ministry of Civil Affairs, the State Population (St. Family Planning Commission, ACWF and the Red Cross Society of China conducted care and support for this group in 2006. They also issued a policy document, and on this basis, the ACWF, MOH and SCAWCO launched a campaign '12.1 Attention to Orphans and Home of Love' for care for orphans and their families. They mobilised 2 million RMB and developed specific work plans in November 2006.
In March 2006, the Ministry of Civil Affairs and 14 other agencies issued a specific 'Suggestion on Strengthening Care to Orphans' (including children orphaned by AIDS), providing favourable conditions in nine aspects of life, including life, education, medical care, recovering, housing and employment. Specific funding of 50 million RMB was allocated, mainly for children orphaned by AIDS in Henan, Yunnan and other provinces to set up advisory centres on better care and placement of children orphaned by AIDS. A multi-level network on displacement of children orphaned by AIDS will be gradually built up, with a vertical working system from province, prefecture, county, township and down to village. At the same time, various forms of displacement models on children affected by AIDS, including adoption, foster family bringing-up and institutional support, were under active exploration. At present 90 per cent of reported children orphaned by AIDS receive family support and schooling. Some older children also received vocational training. The Chinese National Committee for the Care of Children held summer camps annually since 2004 for children for children orphaned by AIDS.
In September 2007, the Ministry of Civil Affairs, SCAWCO, Henan Provincial Government and UNICEF held an international seminar on Care and Placement of Children Orphaned and Made Vulnerable by AIDS in Zhengzhou City, Henan. In 2007, Henan Provincial Government issued a document 'Recommendations on Strengthening Care and Placement of PLHIV', increased local financial inputs, conducted targeted care and support and facilitated the development of care and placement assistance for those living in poverty due to AIDS.
In recent years various China CARES areas explored means of establishing working mechanisms that combine ART, care and self-production support. One-to-one support activities were organized and funds was raised to promote PLHIV and their family's lives, and to help them to undertake self-support production. By March 2007, there were 4,395 reported children double-orphaned by AIDS in 127 China CARES centres; 277 care institutions (such as tender home or home of sunshine) were established; 3,167 orphans (93 per cent of the total school-aged) receiving '2 frees and 1 subsidy (providing free books and waiving other fees and providing life allowance for boarding students)' while 20,879 of the reported PLHIV received life assistance; and 6,255 received assistance to conduct self-support production.
With support of the Comprehensive Family and Community Care Pilot Project for Positive People and Their Families, assistance was provided for family income generating activities and temporary financial relief programs from local civil affairs. In this way, the economic income gap between families affected by AIDS and ordinary families has been narrowed.
Care and support for PLHIV in China CARES village, Daye of Hubei
A relief fund on promoting self-support production of PLHIV has been established in Daye, with initial amount of RMB 800,000 raised and deposited into a special account under centralized management. One-to-one assistance activities are carried out to help PLHIV and their families to improve their living conditions and environment. PLHIV and families capable of economic activities are assisted to develop income-generating projects and families with school-aged children are supported to get their children in school.
Children orphaned by AIDS are provided with subsistence support and monthly living allowances. Financial support is given to hospitalised AIDS patients. The Civil Affairs Bureau helps PLHIV into the social security scheme to ensure their subsistence and livelihood support. Some families affected by AIDS received assistance and production support, amounting 100,000 RMB. A few families have become better off. Some PLHIV supported by institutions have become well-known watermelon producers or pig farmers.
2.5 Surveillance, Testing, Monitoring and Evaluation
The 2004 JAR concluded that the effective analysis, management, integration, sharing and dissemination of such information remained a major challenge. It recommended the development of a national database that integrated information from AIDS case reports, sentinel surveillance, behaviour surveillance and specific surveys, as well as VCT and treatment reporting.
2.5.1 Surveillance system
The national surveillance and sentinel sites were increased from 247 at the end of 2004 to 393 by the end of 2006. The provincial sentinel sites increased from 400 to nearly 500 over the same period, basically covering areas all districts and different focal populations. These provide basic data for the 2007 epidemic estimations.
The national comprehensive surveillance sites increased from 42 in 2004 to 159 in 2006. These are located in 27 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) and cover six population groups at higher risk, namely sex workers, IDUs, STI clinic clients, MSM, long-distance transport workers and adolescent students.
2.5.2 Laboratory testing network
By September 2007, there were 6,066 screening laboratories and 165 confirmation laboratories.
China established and developed an immunology and virology testing platform and conducted research and evaluation into new HIV infections. The central government supported the purchase of 218 flowcytometers for CD4 testing. For patients under treatment, two free CD4 tests are provided each year. Patients receiving CD4 testing before treatment increased from 54.4 per cent in 2005 to the current 85.2 per cent. 90 viral load testing machines were provided to 20 provinces and an AIDS laboratory testing quality control system was established.
2.5.3 Information collection, exchange and utilisation
A Comprehensive Response Management Information System (CRMIS) and the Traditional Chinese Medicine on AIDS Treatment Database and Analyse System were developed to integrate data and information on AIDS. These management systems facilitated data collection and automatically generated reporting tables on HIV response. The collecting, reporting and analysing of standardized information greatly improved efficiency. More data and information is now generated and applied for policy advocacy, resource management, programme planning and monitoring and evaluation. This will assist the 2008 UNGASS report as well.
Information exchange was promoted and facilitated, and large numbers of journals, materials and newsletters were written, published and distributed. A number of AIDS websites have also been established, such as the NCAIDS website. Visitation to the NCAIDS site is more than 2 million since 2002.
2.5.4 Monitoring and evaluation (M&E) systems
The China AIDS Monitoring and Evaluation Protocol (provisional) sets out M&E principles and measures, specific content and indicators, institutional and management mechanism. A national M&E expert team was formed and a national technical support facility was appointed. Clear requirements for the local authorities in establishing specific units and carrying out M&E activities were also compiled.
During 2007 the government undertook training to strengthen M&E capacity at provincial levels and improved coordination of M&E activities in local areas. Various joint cross-sector monitoring, comprehensive technical monitoring and special monitoring missions in particular aspects of programme implementation were conducted for specific aspects of the programme at different levels. These missions assisted in improving the efficiency of monitoring work to facilitate the AIDS response.
2.6 Resource Mobilization and Integration
The 2004 JAR highlighted poor estimation of resource needs, together with inadequate management of resources at provincial level and below as major challenges to the effective allocation of resources to meet local needs for AIDS prevention, treatment and care. A further challenge was to ensure sound management of financial resources.
2.6.1 Resource mobilization
The National Development & Reform Commission established the central debt funds in 2005 to strengthen the health infrastructure in rural areas, in which township-level health centres and county-level hospitals in the China CARES areas were prioritized. While the central level increased its AIDS budget allocations, they also broadened fund-raising channels and utilized resources from international sources.
International inputs to China's AIDS response has increased and now comes through multi-channels. International organizations, developed countries, international non-governmental organizations and some foreign enterprises have also become the important contributors and played supplementary roles.
2.6.2 Resource integration
AIDS resources are drawn from central, local and international sources - central and provincial budgeting account for two-thirds of the total with international sources contributing the remainder. In order to better integrate resources, the central government fully considers national, local and international resources and their adequacy to address the key needs of and issues for different populations and geographical areas. In preparation of its annual budget for AIDS, the Central Government focuses on capacity building, education, interventions, ARV drugs and testing reagents, China CARES operational costs and monitoring and evaluation. In the 2006 central earmarked transfers, ART and follow-up accounted for 30.6 per cent; education and interventions 25.8 per cent; laboratory strengthening 11.5 per cent; China CARES and focal area, 10.8 per cent; screening and VCT, 7.1 per cent; PMTCT 6.2 per cent; blood safety 4.1 per cent; and TCM 3.9 per cent.
External support has been integrated with these priorities for specific populations and at different locations. Global Fund projects in 21 provinces conducted comprehensive treatment and care, comprehensive interventions to IDUs and sex workers, capacity building of civil society organizations and anti-discrimination activities. The China-UK CHARTS project focuses on policy advocacy, information exchange and capacity building, while the US CDC Global AIDS Program is strengthening the surveillance and laboratory systems and the integration of VCT and surveillance.
Under the coordination of SCAWCO and UNAIDS for the UNTG, the UN Joint Programme on AIDS in China (2007 - 2010) was launched, which effectively realigned national and international resources and fully integrated them with national priorities and targets. Significant achievements were made in care for children affect by AIDS, prevention mother-to-child transmission, HIV prevention and treatment for migrant populations by UNICEF and UNFPA supported projects under the framework of UN Joint Programme.
2.6.3 Resource management
The Central Government developed protocols and regulations on budget use and management. The annual central earmarked transfers for AIDS are based on the workload and unit cost planned activities at local level, which are incorporated into the central implementation plan. At the same time central and local governments audit the utilization of their AIDS funds.
For improved prioritization and better utilization of AIDS resources, 13 provinces estimated their needs using the Resource Needs Estimation (RNE) model in 2006 and 2007.
2.7 International Cooperation and Research
China's response to AIDS has expanded from being a recipient of international assistance to itself becoming a provider of international cooperation to other developing countries.
2.7.1 International cooperation
The focus of international support has expanded from serious epidemic provinces such as Yunnan, Guangxi, Xinjiang and Sichuan to low prevalence provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) such as Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Jilin, Qinghai and Ningxia. The area being supported by international cooperation has expanded from monitoring and education to comprehensive prevention and control; from treatment, care and preventive intervention as the focus to encourage and support participation by civil society organizations. The role of international cooperation is no longer limited to technical inputs, but also applies international 'best practice' experience in order to define effective AIDS prevention and control measures in China and facilitates the achievement of the Five-Year Action Plan objectives.
2.7.2 China on the international AIDS stage
China has played an increasing role in providing international assistance to developing counties. It has conducted training courses for HIV professionals from African countries, cooperated in the development of pilot AIDS projects in cross-border areas of China, Myanmar, Laos and Vietnam, donated US$10 million to the Global Fund, demonstrated best practice in China through hosting delegations from countries to undertake study tours of AIDS interventions in China, and actively participated in sharing information at international conferences.
2. 7.3 Scientific research
The Ministry of Science (St Technology has initiated special projects on HIV prevention and AIDS treatment within the National Key Technology Research & Development Program and the National High-tech Research Program (863 Program). There has been progress in the development of AIDS vaccines. The gene vaccines studied have completed phase I clinical testing, which reached international responding standards with other similar vaccines, and phase II has been initiated. There is significant progress in molecular epidemiological survey, identifying local HIV-I sub-type, transformed type and their prevalence characteristics. A batch of important HIV testing reagents was developed. ARV drugs are under active development. The use of traditional Chinese medicine in treatment for AIDS was also explored. More and more applied research facilitated the effective implementation of AIDS responses.
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|












