Chapter 3 SAFER BEHAVIOUR MESSAGES
Drug Abuse
Chapter 3 Safer behaviour messages
Content
Introduction
Cleaning works
Boiling out injection equipment
The bleach procedure
The iodine procedure
The alcohol procedure
Preparing a shot
Self-injecting
Drug emergencies
Introduction
Fatal dilution's
Mixing drugs
Choking
The vital functions
Kiss of life
Heart massage
Overdosing downers
Introduction
High risk situations
Characteristics
What to do
Overdosing stimulants
Introduction
Characteristics
What to do
What not to do
Chasing the Dragon and other ways of administration
Chasing the dragon
Advantages
Disadvantages
Snorting and smoking
Advantages
Disadvantages
SAFER SEX
Introduction
What is a sexually transmitted disease
Other sexually transmitted diseases
Modes of transmission
Unprotected anal sex (arse fucking without a condom)
Unprotected vaginal sex (intercourse, fucking without a condom)
Fellatio (performing oral sex on a man, blow job, sucking off)
Cunnilingus (performing oral sex on a woman, licking, 'going down')
Hand job (jerking someone off)
Finger fucking (in the vagina or anus)
Golden showers and scat (piss and shit)
S/M (Sadomasochism)
Sex toys (dildo's, vibrators etc.)
Massage
French kissing (tongue kissing, passionate kissing)
Group sex (menage a trois, trios, orgies)
Condoms
General information about condoms
With or without lubricant
Flavoured condoms
Female condoms
Extra strong condoms
Instructions for condom use
Tips for sex workers
Negotiation with clients
Sex work and drug use
Condoms
HIV anti-body test. Why, why not?
Like the common cold, AIDS is caused by a virus, the Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). Once you have been infected with HIV there is no cure. However, unlike the virus that causes a common cold, HIV cannot be transmitted through the air. HIV is spread through direct contact with an infected person's blood, semen, or vaginal fluid. It can be transmitted by sharing injection equipment or through sex.
The highest concentrations of HIV are found in the blood, semen and to a lesser extent, vaginal secretions of infected individuals. To contract HIV, the virus must enter your bloodstream.
Persons infected with HIV can look and feel perfectly normal for 6 or more years following exposure. However, during that time they can unknowingly infect other. You can't tell if a person is infected simply by looking at them.
The most effective mode of transmission is blood-to-blood contact. Consequently, someone who shares a syringe with an infected drug user is very likely to become infected.
Sexual transmission is a somewhat less efficient mode of transmission. However, some people have contracted the virus after having sex with an infected individual only once.
If you remember that an infected individual's blood, semen, or vaginal secretions must enter your bloodstream to infect you, it is possible to assess the relative risk of various sexual practices. Any possibility of direct exposure of infected blood, semen or vaginal secretions to your blood is most dangerous. For example, anal intercourse can be very risky because the walls of the rectum are thin and easily torn during intercourse. Any such tears offer direct access for infected semen to enter the bloodstream. Any open sores or cuts on the penis, in the vagina, or anywhere else on the body that come into contact with infected blood, semen or vaginal secretions increase the likelihood of infection. It is also possible for HIV to enter the bloodstream through porous mucous membranes that line the interior of the vagina and penis, but this seems to be a less efficient mode of transmission.
The risk of being infected with HIV is relative. It is affected by circumstances, such as open sores, and by specific practices, such a unprotected sex or the sharing of injection equipment.
(Taken from 'The indigenous Leader Outreach Model' by Wayne Wiebel, USA)
Safer Use
INTRODUCTION
Safer use has been the main emphasis of HIV/AIDS prevention directed at drug users. This could be because drug users are generally more interested in safer use related topics. Although these messages are undeniably important, messages about safer sex are just as important for people using drugs.
This section provides an overview of the most important safer use topics. 'Safer use' is often considered by many, 'as safer injecting' we would like to broaden the concept to also include, 'other means of administering drugs'.
CLEANING WORKS
Most people who use heroin in Europe inject it. Other drugs such as cocaine and amphetamines are also injected. The AIDS epidemic has stressed one important rule:
Always use a new needle and syringe for each injection.
And always try to have a spare new syringe and needle available.
What should you do if new syringes are not at hand?
If you know you will use the syringe again, rinse the syringe and needle directly after injection.
![]() The best thing to do is:
The best thing to do is:![]() Firstly, use a small amount of the drugs in another way i.e. smoking or snorting. (This will counter act withdrawal symptoms.)
Firstly, use a small amount of the drugs in another way i.e. smoking or snorting. (This will counter act withdrawal symptoms.)![]() Secondly, arrange a new syringe.
Secondly, arrange a new syringe.![]() Lastly, use the new syringe to inject the left over drugs.
Lastly, use the new syringe to inject the left over drugs.
![]() The next best thing to do is boiling out the works.
The next best thing to do is boiling out the works.
Other alternatives are:
![]() the bleach procedure.
the bleach procedure.
![]() the iodine procedure.
the iodine procedure.
![]() the alcohol procedure.
the alcohol procedure.
![]() As a last resort: Even rinsing with cold water is better than doing nothing.
As a last resort: Even rinsing with cold water is better than doing nothing.
Boiling out injection equipment
Material required: a stove, pan, water.
Duration: If all equipment is at hand boiling out injection equipment takes about 15 -20 minutes.
Procedure:![]() First, rinse the needle and syringe in cold water 2 times by pulling water up through the needle and flushing it down the drain or toilet.
First, rinse the needle and syringe in cold water 2 times by pulling water up through the needle and flushing it down the drain or toilet.![]() Detach (if possible) the needle from the barrel and pull out the plunger. Ensure that there are no air bubbles left. Place all parts in boiling water for at least 15 minutes.
Detach (if possible) the needle from the barrel and pull out the plunger. Ensure that there are no air bubbles left. Place all parts in boiling water for at least 15 minutes.![]() Allow the parts to cool down before assembling again.
Allow the parts to cool down before assembling again.![]() Before using, rinse the whole syringe another time in cold water.
Before using, rinse the whole syringe another time in cold water.
Advantages:![]() The equipment required is simple and harmless.
The equipment required is simple and harmless.![]() This is the only method of cleaning that is 100% effective against contracting most infections including; HIV, Hepatitis B and bacteria and mould. It is not yet clear if it also kills Hepatitis C.
This is the only method of cleaning that is 100% effective against contracting most infections including; HIV, Hepatitis B and bacteria and mould. It is not yet clear if it also kills Hepatitis C.![]() The spoon (or cooker), can also be disinfected by boiling it together with the syringe.
The spoon (or cooker), can also be disinfected by boiling it together with the syringe.
Disadvantages:![]() A failure which often occurs with this method is that syringes are not properly disinfected. This happens because some people think that placing a syringe in hot water for a minute or so is good enough to disinfect it.
A failure which often occurs with this method is that syringes are not properly disinfected. This happens because some people think that placing a syringe in hot water for a minute or so is good enough to disinfect it.![]() In Europe most drug users shoot up with disposable syringes. These syringes can only be boiled out one to three times: After that the vacuum of the syringe becomes deficient.
In Europe most drug users shoot up with disposable syringes. These syringes can only be boiled out one to three times: After that the vacuum of the syringe becomes deficient.![]() Some syringes perish after being boiled for 15 to 20 minutes.
Some syringes perish after being boiled for 15 to 20 minutes.
The bleach procedure
Material required: ![]() Sodium hypo chloride - Na0C1 (household bleach) in the highest available concentration.
Sodium hypo chloride - Na0C1 (household bleach) in the highest available concentration.![]() A cup or bowl.
A cup or bowl.
Duration: If all the equipment is at hand, the bleach procedure takes about 6 minutes.
Procedure: 2 x water 2 x bleach 2 x water![]() Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.![]() Pull up the bleach through the needle into the syringe, add some air and shake for 30 seconds and squirt out. Repeat this procedure again and don't forget to shake the syringe for 30 seconds.
Pull up the bleach through the needle into the syringe, add some air and shake for 30 seconds and squirt out. Repeat this procedure again and don't forget to shake the syringe for 30 seconds.![]() Rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Advantage:![]() The bleach procedure is cheap and quick.
The bleach procedure is cheap and quick.
Disadvantages:![]() The more traces of blood that remain visible in the syringe, the bigger the chance that the bleach procedure has not been safe. Therefore be sure to pre-rinse well with water and don't forget to vigorously shake the syringe filled with bleach.
The more traces of blood that remain visible in the syringe, the bigger the chance that the bleach procedure has not been safe. Therefore be sure to pre-rinse well with water and don't forget to vigorously shake the syringe filled with bleach.![]() The limited tenability of bleach. In reaction with oxygen, bleach loses its disinfecting quality after three to four weeks.
The limited tenability of bleach. In reaction with oxygen, bleach loses its disinfecting quality after three to four weeks.![]() Not all European countries believe that bleach is 100% safe for disinfecting.
Not all European countries believe that bleach is 100% safe for disinfecting.![]() Bleach can damage some types of syringes.
Bleach can damage some types of syringes.
For optimum result: Pull the syringe apart after disinfecting and rinsing and place in a bowl of bleach for one hour.
![]() Shaking a syringe for 30 seconds does not seem very long but in fact it is; especially if someone is in need of drugs. It is therefore recommended to shake the syringe for 30 seconds while you have time and are not in need of a hit.
Shaking a syringe for 30 seconds does not seem very long but in fact it is; especially if someone is in need of drugs. It is therefore recommended to shake the syringe for 30 seconds while you have time and are not in need of a hit.
The iodine procedure
Material required:
![]() Iodine dilution. Is medically used as a disinfectant for hands, surgical instruments and surgery treatment. A suitable 100 gram dilution contains: 7,5 g poly (1- vinyl-2 pyrrolidine) iodine complex with 10% available iodine (Mw 40000).
Iodine dilution. Is medically used as a disinfectant for hands, surgical instruments and surgery treatment. A suitable 100 gram dilution contains: 7,5 g poly (1- vinyl-2 pyrrolidine) iodine complex with 10% available iodine (Mw 40000).![]() A cup or bowl.
A cup or bowl.
Duration: If all equipment is at hand the iodine procedure takes about 6 minutes.
Procedure: 2 x water 2 x iodine 2 x water![]() Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.![]() Pull up the iodine dilution through the needle and allow it to settle for 2 minutes. Shake syringe well before squirting out. Repeat.
Pull up the iodine dilution through the needle and allow it to settle for 2 minutes. Shake syringe well before squirting out. Repeat.![]() Rinsing: Pull up cold clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Rinsing: Pull up cold clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt it down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Advantages:![]() This procedure is relatively cheap and quick.
This procedure is relatively cheap and quick.![]() Iodine is an accepted and well known substance which is used for disinfecting in surgery treatment.
Iodine is an accepted and well known substance which is used for disinfecting in surgery treatment.![]() There is minimal damage to the quality of the syringe.
There is minimal damage to the quality of the syringe.
Disadvantages:![]() The more traces of blood that remain visible in the syringe, the bigger the chance that the hepatitis virus has not been killed.
The more traces of blood that remain visible in the syringe, the bigger the chance that the hepatitis virus has not been killed.![]() People suffering from iodine allergies and/or malfunctioning of the thyroid gland, should only use this method if they thorouahlv rinse the syringe with water after disinfecting.
People suffering from iodine allergies and/or malfunctioning of the thyroid gland, should only use this method if they thorouahlv rinse the syringe with water after disinfecting.![]() Iodine leaves yellow stains on your skin and clothes
Iodine leaves yellow stains on your skin and clothes
![]() The iodine procedure is not as common as the bleach procedure. The iodine solution mentioned above is approved in Germany as an appropriate substance to disinfect surgery material. A Dutch literature study by the RIVM (National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Hygiene), revealed that there is no research data opposing the use of iodine. Furthermore, iodine is handed out to Swiss prison inmates as part of a first aid kit and used to clean syringes.
The iodine procedure is not as common as the bleach procedure. The iodine solution mentioned above is approved in Germany as an appropriate substance to disinfect surgery material. A Dutch literature study by the RIVM (National Institute of Public Health and Environmental Hygiene), revealed that there is no research data opposing the use of iodine. Furthermore, iodine is handed out to Swiss prison inmates as part of a first aid kit and used to clean syringes.![]() For optimum result: Pull the syringe apart after disinfecting and rinsing and place in a bowl of iodine for one hour.
For optimum result: Pull the syringe apart after disinfecting and rinsing and place in a bowl of iodine for one hour.
The alcohol procedure
Material required: ![]() Medical alcohol (ethanol, isopropanol or n-propanol). Al- cohol for consumption is not suitable for this procedure. In the case of an emergency, consumption alcohol which is at least 70 to 80% strong (preferably clear spirits), could be used.
Medical alcohol (ethanol, isopropanol or n-propanol). Al- cohol for consumption is not suitable for this procedure. In the case of an emergency, consumption alcohol which is at least 70 to 80% strong (preferably clear spirits), could be used.![]() A cup or bowl.
A cup or bowl.
Duration: If all equipment is at hand the alcohol procedure takes about 6 minutes.
Procedure: 2 x water 2 x alcohol 2 x water
![]() Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Pre-rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.![]() Pull up the alcohol through the needle and allow it to settle for 2 minutes. Shake the syringe well before squirting out. Repeat.
Pull up the alcohol through the needle and allow it to settle for 2 minutes. Shake the syringe well before squirting out. Repeat.![]() Rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Rinsing: Pull up cold, clean water through the needle until the syringe is completely filled and squirt down the drain or toilet. Repeat.
Advantages:![]() This is a quick procedure.
This is a quick procedure.![]() Alcohol is very tenable.
Alcohol is very tenable.
Disadvantages:![]() Alcohol is not 100% effective at disinfecting everything i.e. tuberculosis.
Alcohol is not 100% effective at disinfecting everything i.e. tuberculosis.![]() Alcohol severely damages the protection layer on inside of the syringe. This will cause the plunger to run stiffly.
Alcohol severely damages the protection layer on inside of the syringe. This will cause the plunger to run stiffly.
For optimum result: Pull the syringe apart after disinfecting and rinsing and place in a bowl of alcohol for one hour.
Once again: The best and safest way is to always use a clean needle and syringe.
PREPARING A SHOT
The following instructions are written for the ideal situation. Where possible alternatives have been given.
![]() Clean the spoon (or the bottom of a coke can) with water and soap or an alcohol swab.
Clean the spoon (or the bottom of a coke can) with water and soap or an alcohol swab.
![]() Use clean water; cold water from the tap is cleaner than warm water and running water is cleaner than still water.
Use clean water; cold water from the tap is cleaner than warm water and running water is cleaner than still water.![]() Each time you make a new filter (cigarette filter, tampax etc.) make sure it is clean and ensure you have clean hands. The best would be to use a filter for infusion.
Each time you make a new filter (cigarette filter, tampax etc.) make sure it is clean and ensure you have clean hands. The best would be to use a filter for infusion.
![]() See to it that the liquid in the syringe is transparent and without crumbs (if not; cook, shake and/or filter once again). After a while (or even directly), dirt can cause great problems such as the shakes', cardiac diseases, abscesses, embolisms. Also ensure that there are no air bubbles in the syringe.
See to it that the liquid in the syringe is transparent and without crumbs (if not; cook, shake and/or filter once again). After a while (or even directly), dirt can cause great problems such as the shakes', cardiac diseases, abscesses, embolisms. Also ensure that there are no air bubbles in the syringe.
![]() For dissolving brown heroin, it is more preferable to use ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) than lemon juice.
For dissolving brown heroin, it is more preferable to use ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) than lemon juice.
(Taken from L. Synn Stern.)
SELF INJECTING![]() Use a new syringe (or at least a new needle), each time you inject. You will avoid infections (HIV, Hepatitis B/C, bacteria), scars, blue spots, clogged or broken needles.
Use a new syringe (or at least a new needle), each time you inject. You will avoid infections (HIV, Hepatitis B/C, bacteria), scars, blue spots, clogged or broken needles.![]() Choose another spot each time you inject. This means you will have less scars, bruises, abscesses, swellings, withdrawn veins or problems with blood circulation.
Choose another spot each time you inject. This means you will have less scars, bruises, abscesses, swellings, withdrawn veins or problems with blood circulation.![]() Find the biggest vein possible and try to switch between veins each time you inject. If this is impossible, find a new spot a least 2,5 cm (1 inch) from the spot you last injected.
Find the biggest vein possible and try to switch between veins each time you inject. If this is impossible, find a new spot a least 2,5 cm (1 inch) from the spot you last injected.![]() Clean the spot with an alcohol swab and wait till the alcohol has evaporated. This is effective and doesn't hurt when the needle is being inserted.
Clean the spot with an alcohol swab and wait till the alcohol has evaporated. This is effective and doesn't hurt when the needle is being inserted.![]() A tourniquet helps your veins dilate. Use elastic which is easy to loosen e.g. underpants elastic. If you plan to inject in your arm, first let it hang down so that it fills with blood and then apply the tourniquet. Be sure not to tie it too tight or for too long (blood circulation!).
A tourniquet helps your veins dilate. Use elastic which is easy to loosen e.g. underpants elastic. If you plan to inject in your arm, first let it hang down so that it fills with blood and then apply the tourniquet. Be sure not to tie it too tight or for too long (blood circulation!).![]() If you do not succeed in finding a vein, untie the tourniquet, do some physical exercise and tie it once again. Make sure you can loosen the tourniquet before pulling the needle out. For example: Hold one end of the tourniquet in your mouth: Then if you become too stoned your mouth will fall open and automatically untie the tourniquet.
If you do not succeed in finding a vein, untie the tourniquet, do some physical exercise and tie it once again. Make sure you can loosen the tourniquet before pulling the needle out. For example: Hold one end of the tourniquet in your mouth: Then if you become too stoned your mouth will fall open and automatically untie the tourniquet.![]() Do not forget to remove all the air bubbles from the syringe. Keep the syringe up right and if necessary tap the bubbles out out. Push the plunger carefully until no air is left.
Do not forget to remove all the air bubbles from the syringe. Keep the syringe up right and if necessary tap the bubbles out out. Push the plunger carefully until no air is left.![]() It is safer to untie the tourniquet before pushing the plunger down. In the case of overdosing (losing consciousness), a tight tourniquet will almost certainly result in losing the part of the body which has been tied off. Unfortunately for many people this is not possible because if they untie the tourniquet they also 'lose' their vein. Therefore, it is always recommended to have someone with you - just in case.
It is safer to untie the tourniquet before pushing the plunger down. In the case of overdosing (losing consciousness), a tight tourniquet will almost certainly result in losing the part of the body which has been tied off. Unfortunately for many people this is not possible because if they untie the tourniquet they also 'lose' their vein. Therefore, it is always recommended to have someone with you - just in case.![]() Insert the needle at an angle of 15. - 35. (in the direction of your heart), with the point of the needle pointing down. This way of injecting means that the needle slides easily into the vein.
Insert the needle at an angle of 15. - 35. (in the direction of your heart), with the point of the needle pointing down. This way of injecting means that the needle slides easily into the vein.
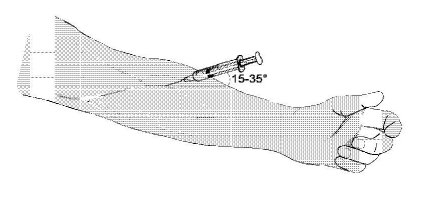
![]() Veins will not roll away if you pull them tight with a finger or the side of your hand: The needle should now be between the tourniquet and the finger/hand that in keeping your vein tight.
Veins will not roll away if you pull them tight with a finger or the side of your hand: The needle should now be between the tourniquet and the finger/hand that in keeping your vein tight.
![]() If you see red blood when you pull back the plunger, you are in a vein. If the blood is pink or the plunger has pushed back by itself, you have hit an artery.
If you see red blood when you pull back the plunger, you are in a vein. If the blood is pink or the plunger has pushed back by itself, you have hit an artery.
If this happens, immediately untie the tourniquet and pull the needle out. Press on the spot with a bandage for at least 5 minutes until you are sure it has stopped bleeding. Hitting an artery can cause serious problems.
![]() When you know your are in a vein push the plunger down slowly. Check several times if you are still in the vein by pulling back the plunger a little. When injecting cocaine, you will not notice if you are next to a vein. If the needle slips out, untie the tourniquet and choose another spot. (The needle will clog less easily if you pull up a small amount of very cold water.) And don't forget to remove the air.
When you know your are in a vein push the plunger down slowly. Check several times if you are still in the vein by pulling back the plunger a little. When injecting cocaine, you will not notice if you are next to a vein. If the needle slips out, untie the tourniquet and choose another spot. (The needle will clog less easily if you pull up a small amount of very cold water.) And don't forget to remove the air.
![]() When you have finished injecting, untie the tourniquet and pull the syringe out in the opposite direction from the way you inserted it. Apply pressure to the injection spot for a short while (for most people this is until the rush has finished). Preferably this should be done with your arm (leg) held up to prevent possible bleeding underneath the skin.
When you have finished injecting, untie the tourniquet and pull the syringe out in the opposite direction from the way you inserted it. Apply pressure to the injection spot for a short while (for most people this is until the rush has finished). Preferably this should be done with your arm (leg) held up to prevent possible bleeding underneath the skin.
![]() If you hit next to a vein or have subcutaneous bleeding, put some ointment (heparin/herodoid), or salted water on the wound and cover with pressure bandages. Missed hits and subcutaneous bleeding can lead to abscesses.
If you hit next to a vein or have subcutaneous bleeding, put some ointment (heparin/herodoid), or salted water on the wound and cover with pressure bandages. Missed hits and subcutaneous bleeding can lead to abscesses.
![]() Don't forget to dispose of your used syringe in a safe way or exchange it for a clean one.
Don't forget to dispose of your used syringe in a safe way or exchange it for a clean one.
(Taken from L. Synn Stern)
DRUG EMERGENCIES
(with contributions from Mainline, Amsterdam and Jan-Hendrik Heudtlass)
Introduction
Death by overdose is an often misinterpreted term. Not many people die from taking too much heroin, or any other drugs, alone. More often drug related deaths are caused by:
![]() fatal dilutions
fatal dilutions ![]() mixing drugs
mixing drugs![]() choking
choking
Fatal dilution's
Illegal drugs are (for reasons of profit), often cut with other substances. Sometimes the cutting is more dangerous than the drug itself and this can lead to casualties.
Mixing drugs
Mixing drugs can be dangerous. In the 'opiate scene' it is common to mix opiates with alcohol and tranquillisers. This combination has frequently lead to dangerous situations - of which overdosing is one.
Choking
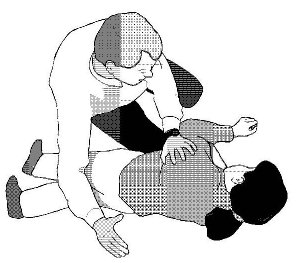
Choking can occur as a result of mixing the above drugs. If people become unconscious they can sometimes throw up. To avoid choking, clear the mouth and throat (for instance with a handkerchief) and place the person in the recovery position. You should only place a person in the recovery position when their breathing and pulse are stable.
The Vital functions
Somebody who is giving first aid in a drug emergency should not waste time on assumptions and speculations. They should act on what they see, the symptoms:
![]() consciousness
consciousness
![]() breathing
breathing
![]() pulse
pulse
Consciousness is checked by shaking and shouting at a person.
If a person is not conscious, try to wake him/her in any way possible. This can be done by slapping the face, dousing with cold water, squeezing hard right under the collarbone or squeezing the septum of the nose.
Breathing is checked by looking, listening or holding the wet back of a hand close to the mouth/nose. If a person is not breathing start mouth to mouth resuscitation (the 'kiss of life').
Kiss of life
![]() Clear the mouth and throat of the victim. Lay the victim on his/her back and tilt head backwards.
Clear the mouth and throat of the victim. Lay the victim on his/her back and tilt head backwards.
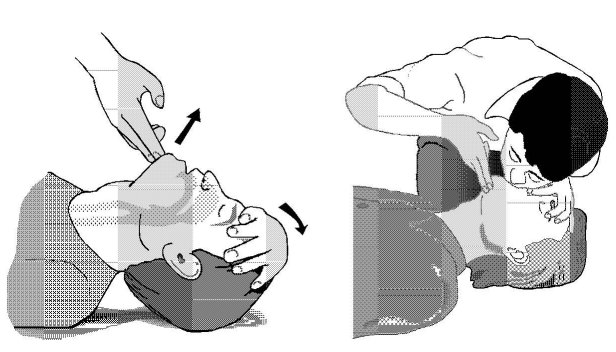
![]() Squeeze nose, inhale deeply and breathe slowly on the mouth of the victim (3 to 5 times).
Squeeze nose, inhale deeply and breathe slowly on the mouth of the victim (3 to 5 times).![]() Check if the breast rises. If not, check the position of the victim. If the person starts breathing of their own volition place in recovery position. If not continue mouth to mouth breathing till help arrives. Check the pulse as well.
Check if the breast rises. If not, check the position of the victim. If the person starts breathing of their own volition place in recovery position. If not continue mouth to mouth breathing till help arrives. Check the pulse as well.
The Pulse is checked by placing two fingers (not a thumb) on the artery in the neck. Check both sides. Only begin a heart massage if you can feel no pulse: Ensure that someone calls a doctor.
Heart massage
![]() Lay the victim on his/her back on a hard surface.
Lay the victim on his/her back on a hard surface.![]() Place the index finger (pointer) on the end of the breastbone (above the solar plexus) and the pointer of the other hand close above it. (This is done to measure the correct spot.)
Place the index finger (pointer) on the end of the breastbone (above the solar plexus) and the pointer of the other hand close above it. (This is done to measure the correct spot.)![]() Make a handball (fist), with your 'first hand' and place it next to pointer on the breast. Then place your 'second hand' over the fisted hand.
Make a handball (fist), with your 'first hand' and place it next to pointer on the breast. Then place your 'second hand' over the fisted hand.
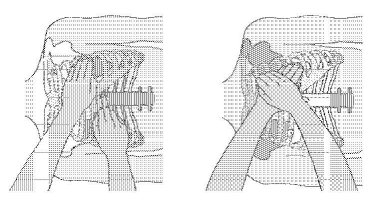
![]() Bend vertically over the victim with your arms completely stretched. Press the breast with short, strong pushes (4 cm), in the direction of the spinal column. Release pressure on the breast immediately but keep hands in the right position.
Bend vertically over the victim with your arms completely stretched. Press the breast with short, strong pushes (4 cm), in the direction of the spinal column. Release pressure on the breast immediately but keep hands in the right position.![]() Repeat pushes 60 to 80 times per minute. If victim is not breathing or has no pulse and you are alone:
Repeat pushes 60 to 80 times per minute. If victim is not breathing or has no pulse and you are alone:![]() Start with 3 to 5 breathes.
Start with 3 to 5 breathes.![]() Then press the breast 15 times. Continue with 2 breathes for every 15 pushes.
Then press the breast 15 times. Continue with 2 breathes for every 15 pushes.![]() Check the pulse on the artery in the neck after 1 minute. Remember to check both sides!
Check the pulse on the artery in the neck after 1 minute. Remember to check both sides!![]() If there is still no pulse, continue heart massage. If there is a pulse, continue mouth to mouth breathing until help arrives.
If there is still no pulse, continue heart massage. If there is a pulse, continue mouth to mouth breathing until help arrives.![]() The kiss of life and heart massage should be exercised before practising. As a peer support initiative, you could organise for somebody from the emergency services or a medical doctor from a drug service to demonstrate these techniques.
The kiss of life and heart massage should be exercised before practising. As a peer support initiative, you could organise for somebody from the emergency services or a medical doctor from a drug service to demonstrate these techniques.
Overdosing downers
Heroin and other opiates are sedatives which effect the central nervous system (brain). The central nervous system regulates (among other things) your breathing and heart pulse. When overdosing with opiates the central nervous system slows down and stops the breathing function and eventually the heart function. Other sedatives such as barbiturates, benzodiazepines and alcohol have similar symptoms when overdosing.
High risk situations
![]() Using drugs when you do not know the quality or purity of High risk them. First try a small dose.
Using drugs when you do not know the quality or purity of High risk them. First try a small dose. ![]() The use of heroin after drinking alcohol and/or using tranquillisers. A person can easily lose consciousness and throw up. The vomit can clog the throat (see above).
The use of heroin after drinking alcohol and/or using tranquillisers. A person can easily lose consciousness and throw up. The vomit can clog the throat (see above).![]() Using drugs after a 'clean period' or after a period of reduced drug use.
Using drugs after a 'clean period' or after a period of reduced drug use.![]() Using drugs alone; no-one is available to give first aid.
Using drugs alone; no-one is available to give first aid.![]() Using heroine after a treatment with an opiate antagonist (see below).
Using heroine after a treatment with an opiate antagonist (see below).
Characteristics
![]() Unconsciousness
Unconsciousness ![]() Slow breathing
Slow breathing![]() Slow pulse
Slow pulse
What to do
![]() Check if the person is really unconscious. Shake and shout at the person.
Check if the person is really unconscious. Shake and shout at the person.![]() If the person is unconscious, try to wake him/her by any means possible (see above).
If the person is unconscious, try to wake him/her by any means possible (see above).![]() The moment the person shows a glimpse of consciousness keep him/her awake by forcing the person to walk, talk, respond etc.
The moment the person shows a glimpse of consciousness keep him/her awake by forcing the person to walk, talk, respond etc.![]() If a person does not become conscious or slips back into unconsciousness again, keep him/her alive with the kiss of life; and if necessary give a heart massage. Ensure someone calls a doctor. A doctor will probably give the person an injection with an opiate antagonist (Narcan etc.).
If a person does not become conscious or slips back into unconsciousness again, keep him/her alive with the kiss of life; and if necessary give a heart massage. Ensure someone calls a doctor. A doctor will probably give the person an injection with an opiate antagonist (Narcan etc.).
![]() It sometimes happens that a doctor treats an overdose of heroine with an antagonist. An injection with opiate antagonist immediately abolishes the effect of opiates. What could happen then is dangerous: The drug user experiences severe withdrawal symptoms and will leave the hospital to experience them. If he/she gets stoned again, there is an enhanced risk of an overdose. While the effects of the antagonist are wearing off (this takes 2 to 3 hours) the initial dose starts working again. This plus the new dose, can easily lead to another overdose.
It sometimes happens that a doctor treats an overdose of heroine with an antagonist. An injection with opiate antagonist immediately abolishes the effect of opiates. What could happen then is dangerous: The drug user experiences severe withdrawal symptoms and will leave the hospital to experience them. If he/she gets stoned again, there is an enhanced risk of an overdose. While the effects of the antagonist are wearing off (this takes 2 to 3 hours) the initial dose starts working again. This plus the new dose, can easily lead to another overdose.
Overdosing stimulants
Commonly used stimulants in the drug scene are cocaine and amphetamines. On a recreational basis hallucinogenic can also have a stimulating effect. It is also possible to overdose on legal substances such as coffee and guarana. With stimulant overdoses, psychological problems are more apparent than physical problems.
Characteristics
![]() Psychological symptoms include: panic, fear, unrest, hypersensitivity and aggression.
Psychological symptoms include: panic, fear, unrest, hypersensitivity and aggression.![]() The somatic symptoms of a stimulant overdose are: sweating, high body temperature (up to fever), fast or irregular pulse, high blood pressure and erratic breathing.
The somatic symptoms of a stimulant overdose are: sweating, high body temperature (up to fever), fast or irregular pulse, high blood pressure and erratic breathing.
What to do
![]() Hallucinogenics: If people show anxiety, approach them quietly. Explain that it is drug related fear that they are experiencing and that it will pass.
Hallucinogenics: If people show anxiety, approach them quietly. Explain that it is drug related fear that they are experiencing and that it will pass.![]() Give them a drink containing some sugar (not coffee or alcohol).
Give them a drink containing some sugar (not coffee or alcohol).![]() Cocaine: A commonly used 'street' treatment for cocaine related anxiety is to give a person a little alcohol or a tranquilliser.
Cocaine: A commonly used 'street' treatment for cocaine related anxiety is to give a person a little alcohol or a tranquilliser.![]() If a person is suffering physical problems call a doctor. If he/she is unconscious, check the vital functions: breathing and pulse (see above).
If a person is suffering physical problems call a doctor. If he/she is unconscious, check the vital functions: breathing and pulse (see above).![]() Do not place the person in a position with their head down What not to do and legs up.
Do not place the person in a position with their head down What not to do and legs up.
CHASING THE DRAGON AND OTHER ROUTES OF ADMINISTRATION
In some countries chasing the dragon has become the most the popular way to administer heroin. At first glance, it seems a simple technique, however it does require some practice to do it cost effectively. (see also: Annex 1 and the video)![]() A portion of heroin is placed on a strip of aluminium foil.
A portion of heroin is placed on a strip of aluminium foil.![]() The underside of the foil is then heated with a modest lighter flame.
The underside of the foil is then heated with a modest lighter flame.![]() The heroin melts and the released vapours are inhaled through a little tube which is held in the mouth.
The heroin melts and the released vapours are inhaled through a little tube which is held in the mouth.
Advantages
![]() The material required is cheap and easy to obtain.
The material required is cheap and easy to obtain. ![]() There is minimal risk of overdosing.
There is minimal risk of overdosing.![]() There is no risk of HIV infection. There are small risks of other infections. (If you share the tube you risk hepatitis infections).
There is no risk of HIV infection. There are small risks of other infections. (If you share the tube you risk hepatitis infections).
Disadvantages
![]() Requires relatively good quality heroin.
Requires relatively good quality heroin. ![]() Only brown heroin is suitable.
Only brown heroin is suitable.![]() It needs some practice to learn to use it cost effectively.
It needs some practice to learn to use it cost effectively.![]() Some adulteration of heroin can cause irritations in the air passage.
Some adulteration of heroin can cause irritations in the air passage.![]() The effectiveness of chasing the dragon is best,when the heroin is diluted with caffeine.
The effectiveness of chasing the dragon is best,when the heroin is diluted with caffeine.
Snorting and smoking
Chasing the dragon is not widespread in most European countries. This is due to bad quality heroin (generally between 2 and 20% purity) and to the relatively isolated position of the drug culture in society. In these countries the most common alternative for injecting heroin is snorting it.![]() Roll some thick paper into a tube or obtain a straw.
Roll some thick paper into a tube or obtain a straw.![]() Chip the substance into fine powder; on for instance a mirror.
Chip the substance into fine powder; on for instance a mirror.![]() Make a line out of the powder.
Make a line out of the powder.![]() Snort the powder through the tube into the nose.
Snort the powder through the tube into the nose.
Advantages
![]() The material required is cheap and easy to obtain.
The material required is cheap and easy to obtain.
![]() This method of administering heroin is less risky than injecting with regard to infections and overdoses.
This method of administering heroin is less risky than injecting with regard to infections and overdoses.
Disadvantages
![]() The drugs and the possible substances that the drugs are cut with, can cause irritation to the nose.
The drugs and the possible substances that the drugs are cut with, can cause irritation to the nose.
In some countries heroin is also smoked in cigarettes. The big disadvantage with smoking it this way is that you lose a lot of heroin. Again, there are health risks associated with what the drugs are cut with.
Safer Sex
INTRODUCTION
What is a sexually transmitted disease?
You can contract HIV (the virus that causes AIDS), or a sexually transmitted disease (STD) by having unprotected sex with someone who is infected. As you may have noticed, the inside of the mouth, vagina, anus and penis are lined with a special skin. This lining is called the mucous membrane. Bacteria and viruses that cause disease, live in this lining. When you have unprotected sex they can move from one person's mucous membrane to another person's mucous membrane. And that is all you need for infection to take place.
Other sexualy transmitted diseases (STDs)
There is no cure for AIDS. It is the disease that most people are afraid of. Other STDs occur more frequently than AIDS. The most common are chlamydia, gonorrhoea (the clap), syphilis, herpes, genital warts and hepatitis.
Some STDs (including HIV) may have no noticeable (initial) symptoms. Therefore, it is important to have yourself tested if you believe you could be infected. (This is even if you are feeling perfectly OK). Most STDs (including syphilis, gonorrhoea and chlamydia) can be easily cured with medicine. This is providing they are detected early enough. If these diseases are not treated in time, they can cause serious harm to your body. For example, if Chlamydia is left untreated it can cause infertility and make it impossible for a woman to bear children.
Other STDs, such as herpes and genital warts, can be treated but cannot be (completely) cured. These will disappear after treatment but may come back later. This is because the virus that causes them lives in blood; where medicine cannot cure it. There is no medical treatment available to cure a hepatitis B infection. The only way to become well again, is to stay in bed for a considerable amount of time.
(Information taken from: The Soa Stichting, The Netherlands)
MODES OF TRANSMISSION
The easiest way to contract HIV or any other STD is through anal sex (arse fucking) and vaginal sex (intercourse). Unless you are using a good condom these are both 'high risk' activities. A good condom, used correctly, can greatly lower your chances of infection; not only from HIV but also other STDs.
Unprotected anal sex (arse fucking without a condom
This is the most risky activity for becoming infected with HIV and other STDs. The lining of the anus is very fragile. Anal intercourse causes damage to the lining allowing sperm infected with HIV or hepatitis to enter the bloodstream. Other STDs, like gonorrhoea and chlamydia can also be transmitted though the mucous membrane.
Many people believe that only the person being penetrated (being fucked) is at risk of infection. This is not true. The active partner who is penetrating, is also at risk of contracting HIV and other STDs: If the head of his penis comes into contact with a virus or bacteria in the other persons body.
![]() Never have unprotected anal sex. You can make anal sex safer, by using an extra-strong condom (for arse fucking) together with a water-based lubricant e.g. K-Y Jelly, Sensilube. Even with a condom, anal sex is never completely safe: This is because condoms can break and/or slide off.
Never have unprotected anal sex. You can make anal sex safer, by using an extra-strong condom (for arse fucking) together with a water-based lubricant e.g. K-Y Jelly, Sensilube. Even with a condom, anal sex is never completely safe: This is because condoms can break and/or slide off.
Unprotected vaginal sex (intercourse/fucking without a condom)
Having vaginal sex without a condom is a high risk activity for becoming infected with HIV. If you already have an STD, the chances of becoming infected with HIV are even greater as the virus can enter more easily through open skin (wounds, sores). HIV is also present in menstrual blood. If a woman is sero-positive, the possibility of passing on HIV are higher if you have sex while she is menstruating.
![]() So our advice is pretty clear: Always use a condom whenever you have anal or vaginal sex.
So our advice is pretty clear: Always use a condom whenever you have anal or vaginal sex.
Fellatio (performing oral sex on a man, blow job, sucking off)
Many people still have questions about the safety of oral sex with regard to HIV transmission. The most up-to-date advice is: As long as sperm does not enter your mouth; you will not come into contact with HIV. One problem with this advice is that it is difficult to know exactly when a man is going to come. Which is why it is preferable to use a condom for oral sex. This is especially important if you have sores in your mouth or if you have bleeding gums.
![]() Using a condom will also protect you from other STDs such as gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and syphilis. It is almost impossible to contract HIV from licking a man's balls or around his anus. Ensure to look out for scratches or sores (to avoid blood contact). Try also to avoid contact with faeces (shit). This will not give you HIV (unless it contains blood), however, it can give you nasty intestinal infections and diseases.
Using a condom will also protect you from other STDs such as gonorrhoea, chlamydia, and syphilis. It is almost impossible to contract HIV from licking a man's balls or around his anus. Ensure to look out for scratches or sores (to avoid blood contact). Try also to avoid contact with faeces (shit). This will not give you HIV (unless it contains blood), however, it can give you nasty intestinal infections and diseases.
Cunnilingus (performing sex on a woman, licking, 'going down')
Even if a women is infected with HIV, her vaginal fluids only contain a small amount of the virus. The chances of becoming infected by 'going down' on a woman are therefore, minimal. However, if a woman is menstruating, oral sex is risky. Contact with menstrual blood can pass on HIV. It is best not to perform oral sex on a woman during her period and the few days either side of her period.
The Herpes virus can also be transmitted during oral sex. Especially if a woman (or man) has blisters, sores or scabs (like cold sores) on or around their vagina, (penis) or mouth. If this is the case you should avoid participating in oral sex.
![]() If you want to be completely safe, use a 'dental dam' for performing oral sex on a woman. It is made from a little sheet of latex rubber that is held over the lips of the vagina during oral sex. Dental dams are sold in sex shops.
If you want to be completely safe, use a 'dental dam' for performing oral sex on a woman. It is made from a little sheet of latex rubber that is held over the lips of the vagina during oral sex. Dental dams are sold in sex shops.
Hand jobs (jerking someone off)
You cannot contract HIV from giving someone a hand job. This is because the virus cannot pass through regular skin. If you have an open sore or blister on your hand, place a plaster or band-aid over it before giving someone a hand job.
Finger fucking (in the vagina or anus)
You cannot contract HIV from inserting fingers or hands (listing') into the vagina or anus; even if the whole hand is put in. As mentioned earlier, the virus cannot enter the body through regular skin. Fisting is more hygienic if you use a thin rubber glove. Also, be sure to use enough water-based lubricant to prevent damage to the inner lining of the anus while fisting.
Golden showers and scat (piss and shit)
Urine (piss) and faeces (shit) contain very small amounts of HIV. This amount can be a problem if urine or faeces have tiny quantities of blood from liver or kidney infections or from haemorrhoids. These invisible drops of blood can expose you to HIV. Urine and faeces can also transmit other STDs such as gonorrhoea. They can also give you severe intestinal infections.
![]() You need not worry if you get piss or shit on your hands or your skin; however do avoid getting them in your nose, eyes, mouth, vagina or anus. All these areas are lined with delicate skin (the mucous membrane). Drinking someone else's piss or eating someone else's shit, poses no serious threat of HIV infection; but does pose a threat for contracting other infections.
You need not worry if you get piss or shit on your hands or your skin; however do avoid getting them in your nose, eyes, mouth, vagina or anus. All these areas are lined with delicate skin (the mucous membrane). Drinking someone else's piss or eating someone else's shit, poses no serious threat of HIV infection; but does pose a threat for contracting other infections.
S/M (Sadomasochism. )
Just like with everything else, S/M can be safe depending on what you do. It is important not to cause bleeding, as infected blood and sperm can enter the body more easily.
![]() If blood gets on the equipment, wash it with soap and water and soak for 10 minutes in 70% alcohol solution before using again. (This solution is for sale in pharmacies).
If blood gets on the equipment, wash it with soap and water and soak for 10 minutes in 70% alcohol solution before using again. (This solution is for sale in pharmacies).
Sex toys (dildo's, vibrators etc.)
There is minimal chance of contracting HIV through using sex toys - although you should be careful if you want to use them with different partners. Try to use only your own personal sex toys and be sure to clean them well with water and soap after use. If you share your toys with others, ensure you use a condom. If you are using a dildo for anal sex, do not put it into your vagina after it has been in your anus. Transferring bacteria from the anus to the vagina can cause nasty infections.
Massage
No risk activity. Touching and rubbing are completely safe and will not give you HIV or any other STDs.
French kissing (tongue kissing, passionate kissing)
Very small concentrations of HIV are found in saliva (spit). This concentration is not large enough to pose a risk of HIV infection through kissing. French kissing is safe for HIV; but not for herpes. Herpes can be contracted if your partner has cold sores, blisters or scabs on his/her mouth or lips.
Group sex (menage a trois, trios, orgies)
Is group sex risky? The answer, depends on what you do. So read over the list again. And be sure to use a NEW condom each time you have intercourse with same or different partner. Make sure everybody agrees in advance.. .and watch out for cheaters!
(Taken from: "Safe Sex", The Soa Stichting, The Netherlands)
CONDOMS
General information about condoms
Condoms, if used properly, are a good way to have sex in a safe way. Although they are not 100% safe; condoms can prevent STDs and unwanted pregnancies.
Different types of condoms are available:
With or without lubricant
Many people prefer to use condoms in combination with a lubricant. The chances of a condom tearing or slipping off is smaller if used in combination with a lubricant. Often condoms are packaged with a water based lubricant already on the condom. Condoms which are suitable for anal sex sometimes contain a separate package of water based lubricant.
Flavoured condoms
Most of the flavoured condoms on the market have not been designed for vaginal use. Flavoured condoms are not lubricated and are suitable for 'blow jobs' (fellatio).
Female condoms
The female condom is not readily available in all European Union member states; and where available, they are expensive. However, the female condom can be convenient for several reasons. The female condom is marketed under the name
"Femidom". It is inserted into the vagina. A rubber ring inside the condom helps keep the condom in the right position. One advantage of the "Femidom" is that it can be inserted into the vagina a long time before actual intercourse takes place.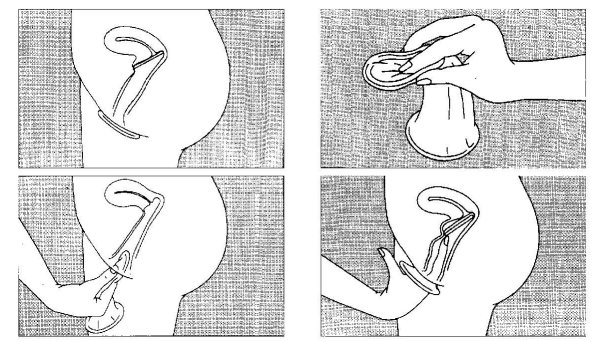
Extra strong condoms
Extra strong condoms are often referred to as gay-condoms. This is incorrect because heterosexuals also practice anal sex. Extra strong condoms are specially designed for anal sex; although they are still not 100% safe. The chance of an 'accident' occurring (i.e. a condom tearing), is considerable if the condom has not been used properly. It is best to use these condoms with extra lubricant.
Instructions for condom use
![]() Check if you have the right condom:
Check if you have the right condom:![]() is it for vaginal or anal sex; if you require it for anal sex, use only special, thicker condoms.
is it for vaginal or anal sex; if you require it for anal sex, use only special, thicker condoms.![]() is it big enough
is it big enough![]() is the brand registered and approved
is the brand registered and approved![]() check the expiry date.
check the expiry date.
![]() Open the package carefully:
Open the package carefully:![]() not with teeth or scissors. This will avoid tearing the condom.
not with teeth or scissors. This will avoid tearing the condom.
![]() Take out the condom:
Take out the condom:![]() be extra careful if you have long nails
be extra careful if you have long nails![]() make sure you have the condom the right way up (i.e. not inside out).
make sure you have the condom the right way up (i.e. not inside out).![]() The tip (for semen reservoir), should be squeezed so that there is no air left
The tip (for semen reservoir), should be squeezed so that there is no air left![]() this will decrease the chance of the condom tearing as the reservoir will not come under pressure
this will decrease the chance of the condom tearing as the reservoir will not come under pressure![]() if the condom has no tip make one yourself by squeezing the air out of the top of the condom (1-3 cm).
if the condom has no tip make one yourself by squeezing the air out of the top of the condom (1-3 cm).
![]() Put the condom on top of the penis and unroll it carefully to the base of the penis
Put the condom on top of the penis and unroll it carefully to the base of the penis![]() wait until the penis is completely hard before putting the condom on
wait until the penis is completely hard before putting the condom on![]() when fully unrolled there is less chance that the condom will slip off
when fully unrolled there is less chance that the condom will slip off![]() again, be careful if you have long nails.
again, be careful if you have long nails.
![]() Use only a water based lubricant
Use only a water based lubricant![]() always use lubricant for anal penetration a non water based lubricant will perish the condom. Do
always use lubricant for anal penetration a non water based lubricant will perish the condom. Do![]() not use Vaseline, hand cream, body lotion, oil or butter.
not use Vaseline, hand cream, body lotion, oil or butter.
![]() Withdraw the penis carefully, immediately after ejaculating
Withdraw the penis carefully, immediately after ejaculating![]() while withdrawing, hold the condom at the base of the penis to avoid it slipping off
while withdrawing, hold the condom at the base of the penis to avoid it slipping off![]() if you wait too long before withdrawing - the penis becomes soft, the condom slips off and the semen drips out.
if you wait too long before withdrawing - the penis becomes soft, the condom slips off and the semen drips out.
![]() Tie a knot in the condom and dispose of it. Do not flush it down the toilet as condoms can block drain pipes.
Tie a knot in the condom and dispose of it. Do not flush it down the toilet as condoms can block drain pipes.
Use a new condom each time you start fucking. Never use two condoms on top of one another: This can cause condoms to tear.
TIPS FOR SEXWORKERS
Before you start working try to:
Negotiation with clients
![]() Set your prices in advance.
Set your prices in advance.
![]() Decide on what you want to do with a client and what you do not want to do with a client.
Decide on what you want to do with a client and what you do not want to do with a client.
![]() Decide on where you want to go (e.g. which parking area or hotel). Do not leave this decision up to the client. Go preferably to a place where others work too.
Decide on where you want to go (e.g. which parking area or hotel). Do not leave this decision up to the client. Go preferably to a place where others work too.
![]() Do a wee before you start working. The rubbing of a penis against a full bladder can cause inflammation of the bladder and urinary infections.
Do a wee before you start working. The rubbing of a penis against a full bladder can cause inflammation of the bladder and urinary infections.
![]() Offer him 'other' sex besides intercourse; such as rubbing his penis between your breasts or thighs. Try to make him horny by talking.
Offer him 'other' sex besides intercourse; such as rubbing his penis between your breasts or thighs. Try to make him horny by talking.
![]() If he refuses to use a condom try to argue that:
If he refuses to use a condom try to argue that:![]() it is for his own safety
it is for his own safety![]() appeal to his masculinity (with condoms it takes longer', 'condoms are sexy' etc.)
appeal to his masculinity (with condoms it takes longer', 'condoms are sexy' etc.)![]() it is for your safety.
it is for your safety.
![]() Make sure you have a stock of condoms, lubricant and paper tissues.
Make sure you have a stock of condoms, lubricant and paper tissues.
![]() Use menthol ointment (for chapped lips) on the inside of your nose. You will smell the client less when you do a blow job and if you are 'dope sick' it will lessen a snivelling nose.
Use menthol ointment (for chapped lips) on the inside of your nose. You will smell the client less when you do a blow job and if you are 'dope sick' it will lessen a snivelling nose.
Sex work and drug use
![]() Try to avoid letting a client know that you use drugs. With this information, a client can tempt you with money and can try to play nasty power games with you.
Try to avoid letting a client know that you use drugs. With this information, a client can tempt you with money and can try to play nasty power games with you.
![]() Insist on receiving your payment in cash, not drugs. Demanding cash makes you more professional and gives you more control.
Insist on receiving your payment in cash, not drugs. Demanding cash makes you more professional and gives you more control.
![]() If you inject, try to avoid scars by changing the injection spot each time. Use new, sharp needles. Rub the injection spot with an ointment such as heparin, Vaseline or haemorrhoid ointment.
If you inject, try to avoid scars by changing the injection spot each time. Use new, sharp needles. Rub the injection spot with an ointment such as heparin, Vaseline or haemorrhoid ointment.
![]() It is difficult to work safely if you are stoned or high (especially on cocaine).
It is difficult to work safely if you are stoned or high (especially on cocaine).
![]() Do not show a client you are dope sick. Avoid sniffing and snivelling. Put some menthol ointment in your nose.
Do not show a client you are dope sick. Avoid sniffing and snivelling. Put some menthol ointment in your nose.
![]() Don't forget to pee between jobs; even if you don't have to.
Don't forget to pee between jobs; even if you don't have to.
![]() Make sure that you are the one who puts the condom on. Condoms
Make sure that you are the one who puts the condom on. Condoms
![]() You can also put a condom on with your mouth. Practise this on a dildo or banana.
You can also put a condom on with your mouth. Practise this on a dildo or banana.
![]() Keep one hand at the base of the penis securing the condom. Your hand can:
Keep one hand at the base of the penis securing the condom. Your hand can:![]() keep the penis hard
keep the penis hard![]() ensure that the condom does not roll up and/or slip off
ensure that the condom does not roll up and/or slip off![]() keep your labia open, to avoid sores
keep your labia open, to avoid sores![]() avoid the penis entering your body too deep.
avoid the penis entering your body too deep.
![]() Take the penis out of your vagina as soon as he has come and hold the condom tight around the penis so that no semen leaks into your body.
Take the penis out of your vagina as soon as he has come and hold the condom tight around the penis so that no semen leaks into your body.
(A selection taken from Als de weg je werk is' written by L. Synn Stern, issued by GGD Rotterdam).
HIV anti-body test
WHY, WHY NOT?
Different people will be thinking about having an anti-body test for different reasons. It is impossible to give concrete reasons for being tested, however here are some points to consider:
![]() If you are ill and a doctor feels that this could be due to HIV, being tested will be an important part of finding out what is wrong.
If you are ill and a doctor feels that this could be due to HIV, being tested will be an important part of finding out what is wrong.
![]() Do not use the test simply to try and find out whether you should practice safer sex. Safer sex is important for everyone. If you are not infected you should stay so; and if you are sero-positive you should avoid infecting other people.
Do not use the test simply to try and find out whether you should practice safer sex. Safer sex is important for everyone. If you are not infected you should stay so; and if you are sero-positive you should avoid infecting other people.
![]() If you are in a relationship, discuss with your partner how being tested might affect you both. In the past, some relationships have been destroyed by the knowledge that one person is positive and the other negative.
If you are in a relationship, discuss with your partner how being tested might affect you both. In the past, some relationships have been destroyed by the knowledge that one person is positive and the other negative.
![]() Being tested may help, if worry is affecting the quality of your life. However, think carefully about whether or not you will be able to cope with a positive result; and would a negative result really stop you worrying?
Being tested may help, if worry is affecting the quality of your life. However, think carefully about whether or not you will be able to cope with a positive result; and would a negative result really stop you worrying?
![]() It may make sense to be tested if you are (or intend) to become pregnant. About 13% of babies born to HIV positive mothers are themselves infected. If you wish to become pregnant, or are in the early stages of pregnancy, there may be considerable pressure on you to take an HIV antibody test. Thorough pre-test counselling is essential so that you understand all the advantages and disadvantages of knowing if you have HIV. This counselling allows you to make informed decisions about your pregnancy.
It may make sense to be tested if you are (or intend) to become pregnant. About 13% of babies born to HIV positive mothers are themselves infected. If you wish to become pregnant, or are in the early stages of pregnancy, there may be considerable pressure on you to take an HIV antibody test. Thorough pre-test counselling is essential so that you understand all the advantages and disadvantages of knowing if you have HIV. This counselling allows you to make informed decisions about your pregnancy.
![]() There is still ignorant and cruel prejudice directed at people with HIV/AIDS and against people who are seen as 'high risk':
There is still ignorant and cruel prejudice directed at people with HIV/AIDS and against people who are seen as 'high risk':![]() People with HIV/AIDS are not allowed to enter certain countries.
People with HIV/AIDS are not allowed to enter certain countries.![]() Some employees have been sacked for being HIV positive.
Some employees have been sacked for being HIV positive.![]() Some people with HIV/AIDS have lost their homes, or faced difficulty in getting accommodation.
Some people with HIV/AIDS have lost their homes, or faced difficulty in getting accommodation.![]() Having a test can have serious implications for insurance and mortgage applications.
Having a test can have serious implications for insurance and mortgage applications.
![]() Think long and hard about taking a test. Don't be pressured into having a test unless you have had enough time to decide whether or not it is the best thing for you. Remember that the test is there for your benefit alone and not for anything or anyone else.
Think long and hard about taking a test. Don't be pressured into having a test unless you have had enough time to decide whether or not it is the best thing for you. Remember that the test is there for your benefit alone and not for anything or anyone else.
![]() Seek advice from your clinic about early intervention treatment, options and support for people who have positive test results. Recent advances in medical treatment of HIV, mean that some medical practitioners now believe it is worth knowing early if you have HIV.
Seek advice from your clinic about early intervention treatment, options and support for people who have positive test results. Recent advances in medical treatment of HIV, mean that some medical practitioners now believe it is worth knowing early if you have HIV.
![]() For example: It is possible for doctors to monitor how well you are, so that if your health deteriorates to a point which may place you at risk of infections like PCP (a virulent pneumonia), drugs can be prescribed which prevent or significantly delay the onset of infection. If your doctor knows that you are at risk, he/she can diagnose and treat any infections more promptly.
For example: It is possible for doctors to monitor how well you are, so that if your health deteriorates to a point which may place you at risk of infections like PCP (a virulent pneumonia), drugs can be prescribed which prevent or significantly delay the onset of infection. If your doctor knows that you are at risk, he/she can diagnose and treat any infections more promptly.
![]() Some healthy people with HIV who have HIV-induced damage to their immune systems may benefit from anti-viral drugs like AZT. If you only discover that you are HIV positive when you start to become ill - you have missed the option of early treatment.
Some healthy people with HIV who have HIV-induced damage to their immune systems may benefit from anti-viral drugs like AZT. If you only discover that you are HIV positive when you start to become ill - you have missed the option of early treatment.
(Taken from: The Terrence Higgins Trust, UK).
Last Updated (Thursday, 06 January 2011 20:56)












