(±)3,4-Methylenedioxymetamphetamine Selectively Damages Central Serotonergic Neurons in Nonhuman Primates
Drug Abuse
first published in Clinical Investigation, JAMA July 1988 vol 260 no 1
Thomas P. Stossel, MD, Section Editor
(±)3,4-Methylenedioxymetamphetamine Selectively Damages Central Serotonergic Neurons in Nonhuman Primates
George A. Ricaurte, MD, PhD; Lysia S. Forno, MD; Mary A. Wilson, Louis E. DeLanney~ PhD;
an Irwin; Mark E. Molliver, IVID; J. William Langston, MID
From the Departments of Neurology and Neuroscience, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore (Drs Ricaurte and Mcilliver and Ms Wilson); the Department of Pathology. Veterans Administration Medical Center, Palo Aft, Calif (Or Forno); and the Institute for Medical Research, San Jose. Calif (Drs Ricaurte, DeLanney. and Langston and Mr Irwin).
Reprint requests to the Department of Neurology. Francis Scott Key Medical Center, The Johns Hopkins Health Center, 4940 Eastern Ave. BaRknore, MID 21224 (Dr Ricaurte).
(±)3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) is a popular recreational drug that has been proposed to be useful as an adjunct to psychotherapy. This study assessed the neurotoxic potential of MDIMA in nonhuman primates.
Monkeys were repeatedly administered doses (2.50, 3.75, and 5.00 mg/kg) of MDMA subcutaneously and analyzed for regional brain content of serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid two weeks later. In all regions of the monkey brain examined, MDMA produced a selective dose-related depletion of serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid. These neurochernical deficits were associated with evidence of structural damage to serotonergic nerve fibers. In addition, MDMA produced pathological changes in nerve cell bodies in the dorsal, but not median, raphe nucleus. These results indicate that MDMA is a selective serotonergic neurotoxin in nonhuman primates and that humans using this drug may be at risk for incurring central serotonergic neuronal damage.
(JAMA 1988;260.51-55)
RECREATIONAL abuse of controlled substance analogues ("designer drugs") potentially'poses a major health problem. " (±)3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), variously known on the street as "Ecstasy," "Adam," or "XTC,"' is an analogue of the controlled, substance (±)3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) Presently, MDMA is one of the more popular recreational drugs in the United States.' It has been estimated that 30 000 capsules of the drug are sold each month (R. K. Siegel, PhD, unpublished data, 1985. It has also been proposed that MDMA may be useful as an adjunct to insight-oriented psychotherapy.' This suggestion is based largely on subjective reports that MDMA improves interpersonal communication - and enhances emotional awareness.
In 1985, the Drug Enforcement Agency placed MDMA on Schedule 1 of. controlled substances, citing increasing recreational use of this drug and expressing concern that MDMA n-dght cause neurological damage.' This concern arose largely because of evidence that MDA (the N-desmethyl derivative of MDRA) destroys central serotonergic nerve terminals in rats.' Recent studies indicate that MDRA, like MDA, is toxic to serotonergic nerve terminals in the rodent brain." However, findings in rats appear to have done little to deter recreational use of MDMA. At least in part, this may be because studies in rodents do not always accurately predict drug toxicity in humans. For example, 1-methyl-4-phenyl1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) is relatively inactive in rats""' but profoundly toxic in primates.""' Conversely, 1,2,3,6-tetrahydro-1-methyl4-(methylpyrrol-2-yl)pyridine, an analogue of MPTP, is very toxic in rodents" but inactive orally in primates." In addition, differences in the way rodents and primates metabolize amphetamines" may alter the neurotoxic effects of these drugs. For these reasons, we thought it critical to assess the neurotoxic activity of MDMA in nonhuman primates.
METHODS
Subjects
Seventeen monkeys were used in this study. Eleven female squirrel monkeys (Saimiri sciur~) 6 to 8 years of age and weighing 0.6 to 0.7 kg were used for neurochemical studies and for anatomic studies of the raphe nuclei. Three female rhesus monkeys (Macaca muULda) 1.5 to 4.0 years of age and weighing 2.5 to 3.5 kg and two female and one male cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) weighing 2.0 to 4.5 kg were used for immunohistochernical studies. No differences in response to MDRA were noted among the three species.
Drug Treatment
The hydrochloride salt of MD.114A was administered subcutaneously twice daily at 0800 and 1700 hours for four consecutive days. This dosing regimen was used to permit comparison of the present results with those previously obtained in rodents. "' For neurochemical studies, eight of 11 squirrel monkeys were administered the following doses of MDMA according to the above-mentioned schedule of drug administration: 2.50 mg/kg (n = 2), 3.75 mgtkg (n = 3), and 5.00 mg/kg (n=U Ile three remaining squirrel monkeys served as untreated controls. For immunohistochemical studies, three of six macaque monkeys were given the high-dose (5.00 mg/kg) regimen of MD?4A; the other three untreated monkeys served as controls.
Two weeks after drug treatment, the monkeys were killed under deep ether anesthesia. The brain was removed from the skull, and the brainstern was dissected away and placed in HK formol saline for later anatomical study. The forebrain was dissected over ice, and the various brain regions were isolated for analysis of monoamine content. Concentrations of. serotonin, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, doparnine, and norepinephrine were measured by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with,electrochemical detection, using the method of Kotake et al' with minor modification.'
Histology
For routine histological studies of the raphe nuclei, the brainstems of three monkeys that had received the 5-mg/kg regimen of MDMA two weeks previously were immersion-fixed in 10% formol saline for one week prior to paraffin embedding and staining. Sections were stained with hematoxyhn-eosm, Luxol fast blue (LFB~- cresyl violet, LFB-periodic acid-Schiff (PAS), or LFB-Bielsehowsky. For immunohistochemical studies of serotonergic nerve fibers in the forebrain, three monkeys that had received the 5-mg/kg regimen of MDMA two weeks previously and three controls were administered the monoamine oxidase inhibitor trans2phenylcyclopropylamine (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) one hour prior to being killed by intracardiac perfusion under deep sodium pentobarbital anesthesia. After the vascular tree was cleared with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline, perfusion was continued with 4% paraformaldehyde, pH 6.5, followed by 4% paraformaldehyde and 0.12% glutaraldehyde (pH 9.5~ Tissue blocks were placed in buffered 4% paraformaldehyde for seven hours and then in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide in phosphatebuffered saline overnight. Frozen sections (30 ~tm) were incubated in an antiserotonin antisera (118) diluted 1:5000 (or in anti-tyrosine hydroxylase antisera diluted 1 U:48 mL) in phosphatebuffered saline with 0.2% octyl phenoxy polyethoxyethanol (Triton X-100) and 1% normal goat serum at 4*C for three days. The antibody was visualized with a peroxidase-labeled avidin-biotin complex (Vector Laboratories Inc, Burlingame, CaM, and staining was enhanced with the osmiophilic reaction sequence of Gerfen.'
Statistics
After a simple one-way analysis of variance showed an F value of P<.05, individual values were compared with the contrbi using a two-tafled Student's t test. Thereafter, regression analysis was performed and the 3 df between groups were partitioned into a regression component (I df) and a. deviation from regression component (2 df).
Materials
Dopamine hydrochloride, norepinephrine hydrochloride, and serotonin creatinine sulfate were purchased from the Sigma Chemical Company, St Louis; MDMA hydrochloride was provided by David Nichols, PhD, Department of Medicinal Chemistry, Purdue University, Lafayette, Ind, and the National Institute of Drug Abuse. Tranylcypromine (tranyl-2-phenyleyclopropylamine) was purchased from Regis Chemical Company, Morton Grove, Ill. The rabbit antiserotonin was generated by H. Lidov against serotonin conjugated to bovine serum albumin with formaldehyde. Rabbit anti-tyrosine hydroxylase antisera was purchased from Eugene Tech International Inc, Allendale, NJ.
RESULTS
Chemistry
Dose Response.-Measurement of serotonin two weeks after drug treatment showed that multiple subcutaneous doses of MDRA (2.50, 3.75, and 5.00 mglkg) produced a dose-related depletion of serotonin in the somatosensory cortex of the monkey, with the lowest dose (2.50 mglkg) producing a 44% depletion and the highest dose (5.00 mg/kg) producing a 90% depletion
(Table 1). Statistical analysis (simple analysis of variance followed linear regression with partitioning of the degrees of freedom into a regression component (I df] and a deviation from regression component (2 df)) revealed that linearity explained virtually all of the variability between doses (r=.97). The deviation from regression component was not statistically significant (F2,8 = 2.28; P >. 05~
Regional Effects. Multiple doses of MDMA also produced large depletions of serotonin in the caudate nucleus, putamen, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and thalamus of the monkey (Table 2). One of the most severely affected areas was the cerebral cortex (Table 2), where the lowest dose (2.5 mg/kg) of MDMA produced a 44% depletion of serotonin (Table 4
Other Markers. Measurement of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid, another chemical marker for serotonergic nerve fibers, showed that multiple doses of MDMA also markedly reduced the concentration of this compound (Table U Concentrations of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid were reduced by 84% in the neocortex, 76% in the caudate nucleus, 75% in the hippocampus, and 40% in the hypothalamus.
Selectivity. Measurement of dopamine and norepinephrine concentrations in monkeys receiving the highest dose (5 mg/kg) showed that MDMA produced no depletion of doparnine or norepinephrine (Table 4)
Morphology
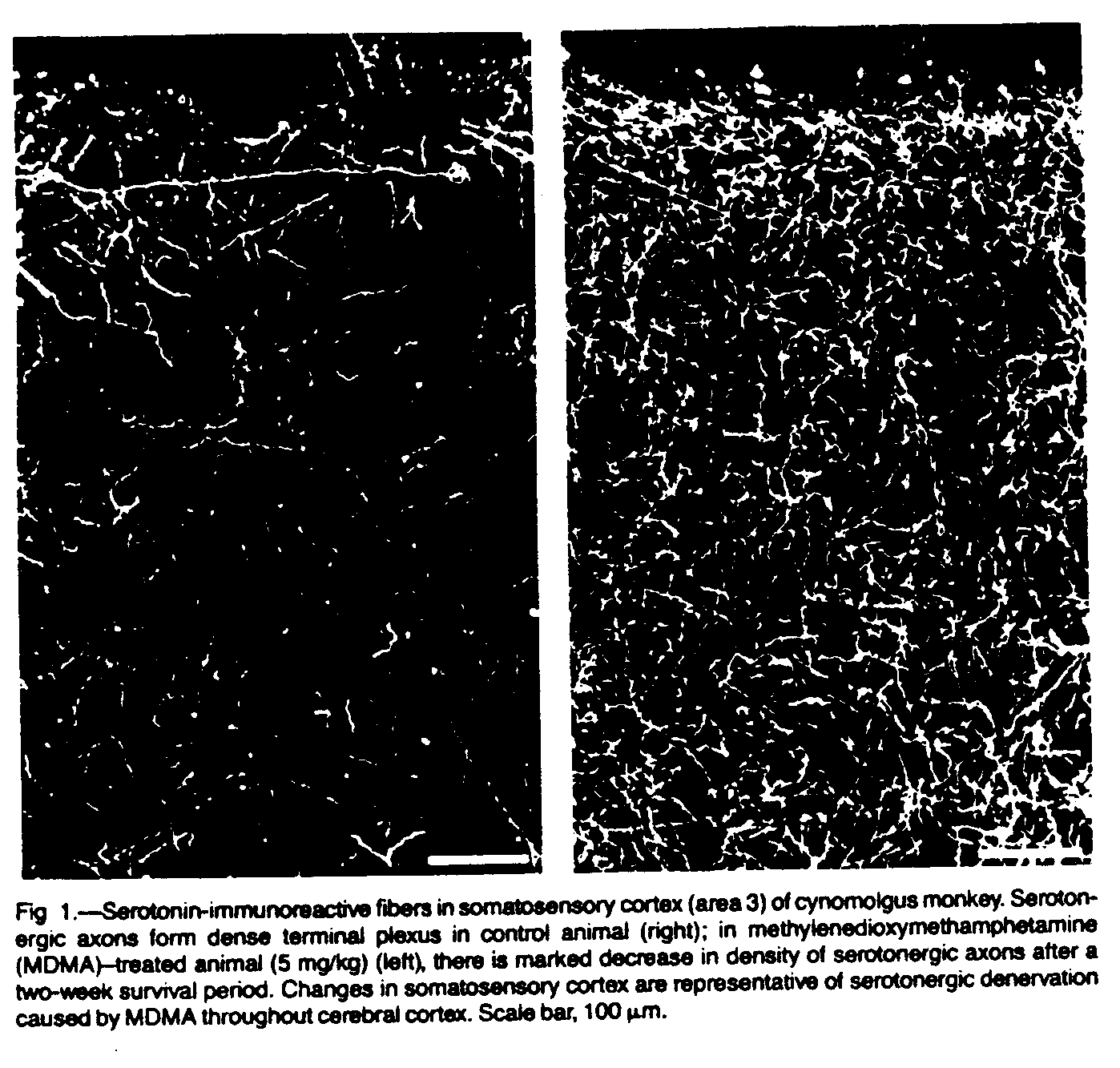
Nerve Fibers.-Immunohistochemical studies performed to assess the structural integrity of serotonergic nerve fiber projections to the forebrain demonstrated a marked reduction in the number arid density of serotonininimunoreactive axons throughout the cerebral cortex of three of three monkeys receiving the 5-mg/kg dose of MDMA (Fig 1). In addition, at higher power, some serotonergic axons appeared swollen and misshapen. Staining with an antibody to tyrosine hydroxylase revealed no evidence of damage to catecholamine-containing nerve fibers in the cerebral cortex.
Cell Bodies. Examination of nerve cell bodies in the raphe nuclei of the monkeys receiving the highest dose of MDMA (5 mg/kg) showed that while MDMA produced no obvious cell loss in either the dorsal or median raphe nuclei, the drug induced striking cytopathological changes in nerve cells of the dorsal raphe nucleus. In three of three of these animals, hematoxylineosin-,gtained paraffin sections of the dorsal raphe nucleus showed numerous, somewhat shrunken nerve cells that contained brownish-red spherical cytoplasmic inclusions that displaced the nucleus to the periphery of the cell (Fig 2, top left). In LFB-PAS-stained sections, the inclusions appeared granular and were vividly PAS positive (Fig 2, bottom right). This staining reaction suggests the presence of an increised amount of ceroid or lipofuscin, possibly due to lipid peroxidation of cell components and subsequent phagolysosomal activity. The presence of Upofuscin within the inclus ions was confirmed by a numbicr of staining procedures. Specifically, the granules were autofluorescent in ultraviolet light, acid fast in Ziehl-Nielsen stain for lipofusein, and positive with Schmori's reaction and Sudan Black B stain. Glycogen did not account for the staining, as demonstrated in PAS stain with and without diastase.
No abnormal inclusion-bearing cells were found in the median raphe nucleus, in other raphe nuclei, or in nonserotonergic nuclei such as the substantia nigra or locus ceruleus. No similar inclusions were found in ten control monkeys of varying ages (including three 15- to 20year-old monkeys), although some increased lipofuscin pigment was occasionally found in the older animals. (Seven of these ten animals were not formally part of the present study but had served as controls in other experiments. The brains of these seven animals were fixed by immersion in 10% formol saline.)
COMMENT
The major finding of this study is that central serotonergic neurons in nonhuman primates are highly vulnerable to the toxic effects of MDMA. Compared with the rodent,"" the primate has been found to be approximately four to eight times more sensitive. In the monkey, a dose of 2.5 mg/kg produces a 44% depletion of serotonin in the cerebral cortex (Table 11 By contrast, in the rat a 10- to 20-mg/kg dose is required to produce a comparable effect." Also of note is the fact that in the primate small increments in dose from 2.50 mg/kg to 3.75 and 5.00 mg/kg produced 78% and 90% depletions of serotonin, respectively (Table 1). This indicates that the doseresponse curve of MDMA in the monkey is steep, suggesting that the margin of safety of MDMA in humans may be narrow.
The striking loss of serotonin-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the cerebral cortex of the MDMA-treated primate (Fig 1) suggests that MDMA produces a longterm depletion of serotonin by actually damaging serotonergic nerve fibers. Axonal damage is further suggested by the swollen and distorted appearance of some of the remaining fibers. Morphological evidence of nerve fiber damage is important because it suggests that the prolonged depletion of serotonin induced by MDMA is not merely due to a pharmacologic action of the drug, but rather represents a neurotoxic effect. Anatomical studies in rats have led to a similar conclusion. `*
It is not yet known whether the effects of MDMA on serotonergic neurons in the primate are permanent or reversible. Under some circumstances, regeneration of serotonergic nerve fibers in the central nervous system can take place.' However, for axon regrowth to occur, the cell body must be preserved. It remains to be determined if serotonin-containing cell bodies in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the MDMAtreated primate survive beyond two weeks. If they do, and if regeneration of nerve fibers takes place, it is still not certain that the new fibers would establish normal connections. For functional integrity to be maintained, normal connections would need to be reestablished. It will be important to determine if this occurs in MDMAtreated animals.
This study provides the first direct evidence that serotonergic cell bodies, as well as nerve fibers, are affected by MDMA. As shown in Fig 2, the pathological change in cell bodies involves formation of intracytoplasmic inclusions. These inclusions resemble the more eosinophilic but usually PAS-negative inclusions recently described in monkeys given MP`TP,' a compound that destroys nigral cell bodies."' Whether the inclusions in the MDMA-treated primate herald nerve cell death or reflect a metabolic response of the cell body to axonal injury is not yet known but needs to be ascertained because, if cell-body death occurs, the possibility of axonal regeneration would be precluded.
The fact that abnormal inclusions were found in nerve cells of the dorsal, but not median, raphe nucleus is noteworthy because it suggests that MDMA selectively damages a particular subset of Serotonergic neurons in the brain (ie, the B7 group of Dahlstrom and Fuxe). That this is the case is also suggested by the recent finding in the rat that serotonergic nerve fibers arising from the dorsal, but not median, raphe nucleus are damaged by MDMA." Taken together, these findings indicate that MDMA is likely to be a valuable new tool for further defining the functional anatomy of different serotonergic cell groups in the mammalian brain.
The mechanism by which MDMA exerts its toxic effects on central serotonergic neurons is at present not well understood. Like a number of other ring-substituted amphetamines (eg, p-chloroamphetamine, fenfluran-line hydrochloride, MDA), MDMA appears to release serotonin." Commins and colleagues' have proposed that MDMA and related compounds destroy serotonergic neurons by releasing large amounts of serotonin and inducing endogenous formation of 5,6dihydroxytryptamine, a well-known serotonergic neurotoxin.' However, other investigators' maintain that the degenerative effects of ring-substituted amphetamines may be mediated by a toxic metabolite. It remains to be determined which, if either, of these possibilities proves correct.
The results of this study raise concern that humans presently using MDMA may be incurring serotonergic neuronal damage. The fact that monkeys are considerably more sensitive than rats to the toxic effects of MDMA suggests that humans may be even more sensitive.
Before extrapolating the present results to humans, however, it should be noted that monkeys were given multiple rather than single doses of MDMA and that the drug was given subcutaneously rather than orally. Humans generally take MDMA via the oral route and use single 1.7- to 2.7-mg/kg doses of the drug, usually weeks apart, although some individuals have used higher and more frequent doses.' It remains to be determined if administration of MDMA to monkeys in a pattern identical to that used by humans produces similar neurotoxicity. In this regard, however, it is important to bear in mind that the sensitivity of human and nonhuman primates to the toxic effects of MDMA may not be the same. In fact, humans are generally regarded as being more sensitive than monkeys to the toxic effects of drugs.
For example, humans are fivefold to tenfold more sensitive than monkeys to the toxic effects of MPTP (compare references 19 and 35). In view of these considerations, it would seem prudent for humans to exercise caution in the use of MDMA. Caution may also be warranted in the use of fenfluramine, a ring-substituted amphetamine that is closely related to MDMA and is currently prescribed for obesity' and autism.'
From an experimental standpoint, MDMA appears to hold promise as a systemically active toxin that can be used to study the functional consequences of altered serotonergic neurotransmission in higher animals. Clinically, it will be important to determine if humans who have taken MDMA show biochemical signs of serotonergic toxicity (eg, decreased 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid concentration in their cerebrospinal fluid). If they do, it will be critical to ascertain if these individuals have any functional impairment. In particular such individuals will need to be
evaluated for possible disorders of sleep, mood, sexual function, appetite regulation, or pain perception, since central serotonergic neurons have been implicated in all of these functions." These studies could offer the unique opportunity to better delineate the neurobiology of central serotonergic neurons in the human brain, something that until now has not been possible.
This work was supported in part by the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies, Sarasota, Fla; the Veterans Administration Medical Research Program; National Institutes of Health grant NS21011 (M.E.M.); and California Public Health Foundation Ltd subcontract 091A-701. One of the authors (M.A. W.) was supported by the L. P. Markey Fund.
We thank Lorrene Davis-Ritchie, ZoAnn McBride, David Rosner, and Patrice Carr for expert technical assistance.
Roferences
1. Ziporyn T: A growing industry and menace: Makeshift laboratory's designer drugs. JAMA
2. Baum RM: New variety of street drugs poses
3. Hagerty C: 'Designer Drug' Enforcement Act
4. Seymour RB: MDMA. San Francisco, Haighthbury Publications, 1986.
5. PBarnes DM: New data intensify the agony over ecstasy, Science 19M;239:864-866.
6. Greer G, Thlbert R: Subjective 2~rts of the effects of MDMA in 2 clinical setting. J Psychoactive Drugs 1986;18:319-V7,
7. Cotton R: In the matter of MDMA scheduling.Brief including proposed findings of fact and conclusions of law on behalf of Drs Greer and Grinspoon,and Professors Bakalar and Roberts. Dewey, Bailantine, Bushby, Palmer and Wood, 1775 Pennsylvania Ave NW, Washington, DC 20006, Jan 15,
8. Lawn JC: Schedules of controlled substances:
15. Battaglia G, Yeh SY, O'Hearn E, et al: 3,4-Methylenedioxymethimphetamine and 3,4methylenedioxyamphetamine destroy serotonin terminals in rat brain: Quantification of neurodegeneration by measurement of [ a Hlparoxetine-labeled serotonin uptake sites. J Pharmacol Exp !.w~1988;242:911-916.
16. Chiueh CC, Markey SP, Burns RS, et al: ethyi4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetmhydropyridine, a parkinsonian syndrome-causing agent in man and monkey, produces different effects in the guinea pig and mt. Pharmacologis 1983;25:131-138. ?
17. Boyce S, Kelley E, Reavill C, et al: Repeated administration of N-methyl4-phenyl-1,2.5,6-tetrahydropyridine to rats is not toxic to striatal dopamine neurones. Biochem Pharmacol 1984; 33:1747-1752.
18. Burns RS, Chieuh CC, Markey SP, et al: A primate model of parkinsonism. Selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the pars compacts of the substantia nigra by N-methyl-4phenyi1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 19M 80: 45464550.
19. Langston JW, Forno LS, Rebert CS, et al: Selective nigral toxicity after systemic administration of 1-methy]4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) in the squirrel monkey, Brain Res 1984;292:390-394.
20. Finnegan KT, Irwin 1, DeLanney LE, et al: 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydre-l-methyl4-(methylpyrrol2-yl)pyridine: Studies on the mechanism ofaction of MPTP. JPharmacol Exp Ther 1988;242:1144-1151. 21. Wilkening D, Vernier VG, Arthaud LE, et al: A parkinson-like neurologic deficit in primates is caused by a novel 4-substituted piperidine. Brain Res 1986;368:239-246.
22. Caldwell J, Dring LG, Williams RT: Metabolism of( 14CImethamphetamine in man, the guinea pig and the rat. Biochem J 1976,129:11-21.
23. Kotake C, Heffner T. Vosmer G, et al: Determination of dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and their major metabolic products in mt brain by reverse-phase ion-pair high performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Pharmacol B iochem Behav 1985;22:85-90.
24. Ricaurte GA, Irwin 1. Forno LS, et al: Aging and 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. B rain Res 1987;403:4351.
25. Gerfen C: The neostriatal mosaic: 1. Compartmental organization of projections from the striaturn to the substantia nigra in the rat. I Comp Neuroi 1985:236:454-463.
26. Zhou FC, Azmitia EC: Induced homotypic collateral sprouting ofserotonergic fibers in the hippocampus of mt. Brain Res 1984;308:53-62.
27. Forno LS, Langston JW, DeLanney LE, et al: Locus ceruleus lesions and eosinophilic inclusions in MPTP-treated monkeys. Ann Neuroi 1986;20:449455.
28. Manmounas LA, Molliver ME: Dual serotonergic projections to forebrain have separate origins in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei: Retrograde transport after selective axonal ablation by pchloroamphetamine 1,PCA).* Soc Neurosci Abstr 1987;13:907.
29. Sanders-Bush E, Sulser F: P-chloroamphetamine: In vivo investigations on the mechanism of action of the selective depletion of cerebral seroto
30. Fuller RW, Perry KW, Molloy B: Reversible and iirreversible phases of gerotonin depletion by 4-chloroamphetamine. Eur,J Pharmacol 1975; :11
31. Nichols DE, Lloyd DH, Hoffman AJ, et al: Effect of certain hallucinogenic amphetamine analogs on the release of ['H Iserotonin from rat brain synaptosomes. JMed Chem 1986;25:530-536. '?
32. Commins'B_,=xt I =,osmer G, et al: Endoie nously produced 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine may mediate the neurotoxic effects of para-chloroamphetamine. Brain Res 1987;403:7-14.
33. Baumgarten HG, Klemm HP, Lachenmayer L, et al: Mode and mechanism of action of n rotoxic indoleamines: A review and a progress report. A nn NY Acad Sci 1978;305:3-24.
34. Molliver ME, O'Hearn E, Battaglia G. et a]: Direct intracerebral administration of MDA and MDMA does not produce serotonin neurotoxicity. Soc Neurosci Abstr 1986; 12:1234.
35. Langston JW, Ballard PA, Tetrud JW, et al: Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 1983; 219:979-980.
36. Craighead LW, Stunkard AJ, O'Brien R: Behavior therapy and pharmacotherapy for obe Arch Gen Psychiatry 1981;38:763-768.
37. Ritvo ER, Freeman DJ, Geller E, et al: Effects ofenfluramine on 14 outpatients with the syndrome of autism. J Am Acad Child Psychiatry 1983:22:549-556.
38. Barchas J, Usdin E (eds): Serotonin and lighavior. New York, Academic Press Inc, 1973. D9. Messing RB, Pettibone DJ, Kaufman N, et al: Behavioral effects of serotonin neurotoxin: An overview. Ann NYAcadSci 1978;305:480496. 1
Last Updated (Monday, 20 December 2010 19:42)












